Call +(254) 703 030 000 / 751 483 999 / 721 704 777
- Home
- Raw Materials
- Metals
- Stainless Steel
- Stainless Steel Sheets Plates
.....Read More
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different grades of stainless steel sheets and plates?
Stainless steel sheets and plates are categorized into different grades based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. The primary grades include:
1. **Austenitic Stainless Steel**:
- **304/304L**: Most common, offers good corrosion resistance, formability, and weldability. 304L has lower carbon content for better welding.
- **316/316L**: Contains molybdenum for enhanced corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides. 316L is the low-carbon version.
- **310/310S**: High temperature resistance, used in heat exchangers and furnaces.
2. **Ferritic Stainless Steel**:
- **430**: Good corrosion resistance and formability, used in automotive trim and appliances.
- **409**: Contains less chromium, used in exhaust systems and other high-temperature applications.
3. **Martensitic Stainless Steel**:
- **410**: Basic martensitic grade, offers high strength and moderate corrosion resistance, used in cutlery and surgical instruments.
- **420**: Higher carbon content for increased hardness, used in cutlery and surgical tools.
4. **Duplex Stainless Steel**:
- **2205**: Combines austenitic and ferritic properties, offers high strength and excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking.
- **2507**: Super duplex grade with higher corrosion resistance, used in chemical processing and marine applications.
5. **Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel**:
- **17-4 PH**: Combines high strength and corrosion resistance, used in aerospace and chemical industries.
Each grade is selected based on specific requirements such as corrosion resistance, strength, temperature resistance, and formability. The choice depends on the intended application and environmental conditions.
How do stainless steel sheets resist corrosion?
Stainless steel sheets resist corrosion primarily due to the presence of chromium, which is a key alloying element. When stainless steel is exposed to oxygen, chromium reacts with it to form a thin, stable layer of chromium oxide on the surface. This passive film is highly adherent and self-repairing, meaning that if the surface is scratched or damaged, the chromium in the steel will react with oxygen to quickly reform the protective layer, preventing further corrosion.
The effectiveness of this passive layer is enhanced by the presence of other alloying elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and nitrogen. Nickel improves the overall corrosion resistance and enhances the stability of the passive film, especially in acidic environments. Molybdenum increases resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, which are localized forms of corrosion that can occur in chloride-rich environments, such as seawater. Nitrogen also contributes to the strength and pitting resistance of stainless steel.
The microstructure of stainless steel, which can be austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, or duplex, also plays a role in its corrosion resistance. Austenitic stainless steels, which contain higher levels of chromium and nickel, are particularly known for their excellent corrosion resistance and are widely used in various applications.
Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive agents, can influence the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. However, the inherent properties of stainless steel, particularly the formation of the chromium oxide layer, provide a robust defense against corrosion, making it a preferred material in industries where durability and longevity are critical.
What are the standard sizes of stainless steel sheets and plates?
Standard sizes for stainless steel sheets and plates typically vary based on thickness, width, and length. Common thicknesses range from 0.4 mm to 6 mm for sheets and 6 mm and above for plates. Standard widths are usually 1000 mm, 1219 mm (commonly referred to as 48 inches), and 1500 mm. Lengths are often 2000 mm, 2438 mm (commonly referred to as 96 inches), and 3000 mm. However, custom sizes can be produced based on specific requirements.
How are architectural stainless steel sheets used in construction?
Architectural stainless steel sheets are widely used in construction due to their durability, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to corrosion. These sheets are employed in various applications, including cladding, roofing, and interior design.
In cladding, stainless steel sheets provide a sleek, modern facade for buildings. They protect the structure from environmental elements while offering a reflective surface that enhances natural light. The sheets can be customized with different finishes, such as brushed, polished, or patterned, to achieve the desired architectural effect.
For roofing, stainless steel sheets are chosen for their longevity and minimal maintenance requirements. They are lightweight yet strong, making them suitable for both flat and pitched roofs. The material's resistance to rust and staining ensures that the roof maintains its appearance over time.
Inside buildings, stainless steel sheets are used for wall panels, elevator interiors, and countertops. Their hygienic properties make them ideal for kitchens and bathrooms, where cleanliness is paramount. The sheets can be easily cleaned and do not harbor bacteria, making them a popular choice in hospitals and food processing facilities.
Additionally, stainless steel sheets are used in structural applications, such as support beams and columns, due to their high tensile strength. They contribute to the overall stability and safety of the building.
In summary, architectural stainless steel sheets are versatile materials in construction, offering both functional and aesthetic benefits. Their use in cladding, roofing, interior design, and structural components highlights their importance in modern architecture.
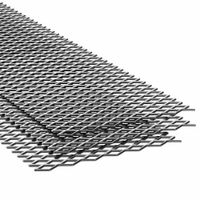
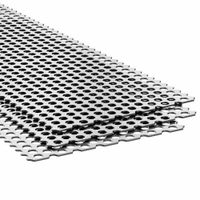
What is the difference between expanded and perforated stainless steel sheets?
Expanded stainless steel sheets are created by cutting and stretching the metal to form a mesh-like pattern, resulting in a single piece with no welds or joints. This process increases the sheet's strength-to-weight ratio and provides excellent rigidity and durability. Expanded sheets are often used for applications requiring ventilation, filtration, or decorative purposes, as they allow light, air, and sound to pass through while maintaining structural integrity.
Perforated stainless steel sheets, on the other hand, are produced by punching holes into the metal sheet in a specific pattern. These holes can vary in size, shape, and distribution, offering a wide range of design possibilities. Perforated sheets are commonly used for aesthetic applications, noise reduction, and as screens or filters. They provide good airflow and light passage but may not be as strong as expanded sheets due to the material removed during the perforation process.
In summary, the primary difference lies in their manufacturing processes and resulting structures: expanded sheets are cut and stretched to form a continuous mesh, while perforated sheets have holes punched into them. This leads to differences in strength, weight, and application suitability.
How do you maintain and clean stainless steel sheets and plates?
To maintain and clean stainless steel sheets and plates, follow these steps:
1. **Regular Cleaning**: Use warm water and a mild detergent. Apply with a soft cloth or sponge, then rinse thoroughly with clean water. Dry with a soft towel to prevent water spots.
2. **Stain Removal**: For stubborn stains, use a paste of baking soda and water. Apply gently with a soft cloth, then rinse and dry.
3. **Avoid Abrasives**: Do not use steel wool or abrasive cleaners, as they can scratch the surface. Opt for non-abrasive cleaning pads if necessary.
4. **Fingerprints and Smudges**: Use a glass cleaner or a solution of vinegar and water. Spray lightly and wipe with a microfiber cloth.
5. **Polishing**: Use a stainless steel polish or olive oil to enhance shine. Apply with a soft cloth, following the grain of the steel, then buff to a shine.
6. **Rust Prevention**: Ensure the surface is dry after cleaning. For added protection, apply a thin layer of mineral oil or a specialized stainless steel protector.
7. **Avoid Chlorides**: Keep stainless steel away from bleach and chloride-based cleaners, which can cause corrosion.
8. **Regular Inspection**: Check for signs of damage or corrosion regularly. Address issues promptly to prevent further deterioration.
9. **Environmental Considerations**: Protect from harsh environments, such as saltwater or industrial pollutants, which can accelerate corrosion.
10. **Storage**: Store in a dry, clean area. Use protective coverings if necessary to prevent scratches and exposure to contaminants.
By following these steps, you can maintain the appearance and longevity of stainless steel sheets and plates.
What are the applications of stainless steel sheets in various industries?
Stainless steel sheets are widely used across various industries due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. In the construction industry, they are employed for cladding, roofing, and interior design elements, providing both structural integrity and a modern look. The automotive industry utilizes stainless steel sheets for manufacturing exhaust systems, trim, and structural components, benefiting from their resistance to heat and corrosion.
In the food and beverage industry, stainless steel sheets are essential for equipment like tanks, countertops, and processing machinery, ensuring hygiene and ease of cleaning. The chemical and petrochemical industries rely on them for storage tanks, pipelines, and reactors, where resistance to corrosive substances is crucial.
The medical field uses stainless steel sheets for surgical instruments, medical devices, and hospital equipment, taking advantage of their sterilization capabilities and non-reactive nature. In the energy sector, they are used in the construction of power plants, particularly in nuclear and renewable energy applications, due to their strength and resistance to extreme conditions.
The aerospace industry incorporates stainless steel sheets in aircraft components, offering a balance of strength and weight. In the marine industry, they are used for shipbuilding and offshore platforms, where exposure to saltwater demands high corrosion resistance.
Lastly, in the consumer goods sector, stainless steel sheets are found in appliances, kitchenware, and electronics, valued for their aesthetic appeal and longevity. Overall, the versatility and performance of stainless steel sheets make them indispensable across these diverse applications.