Call +(254) 703 030 000 / 751 483 999 / 721 704 777
.....Read More
Frequently Asked Questions
What are double-end end mills used for?
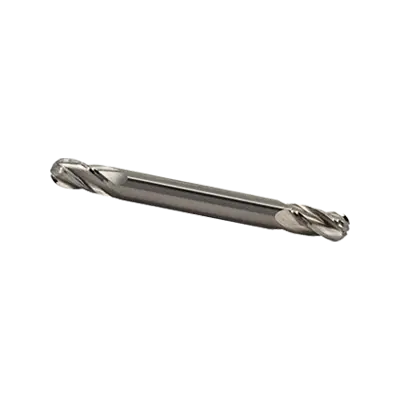
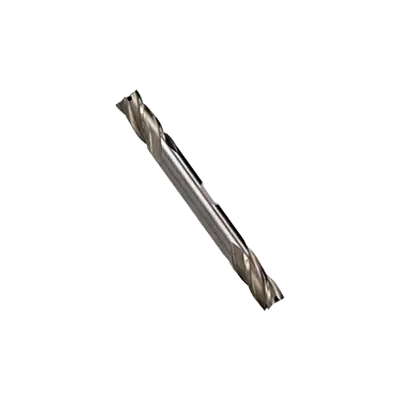
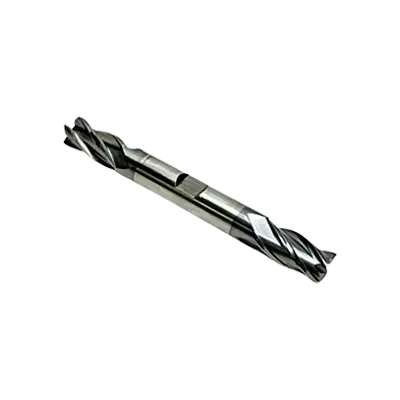
Double-end end mills are cutting tools used in milling applications, featuring cutting edges on both ends of the tool. This design allows for increased tool life and cost efficiency, as both ends can be used before the tool needs to be replaced. They are typically used in CNC machines and manual milling machines for various operations such as slotting, profiling, and contouring.
The primary advantage of double-end end mills is their cost-effectiveness. By having two cutting ends, they effectively double the tool's lifespan compared to single-end end mills, reducing the frequency of tool changes and downtime. This is particularly beneficial in high-volume production environments where tool longevity and efficiency are critical.
Double-end end mills are available in various shapes and sizes, including square end, ball nose, and corner radius, to accommodate different milling tasks. They are made from materials like high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and cobalt, each offering different levels of hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance, making them suitable for cutting a wide range of materials, from soft metals like aluminum to harder materials like stainless steel.
These tools are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and mold-making, where precision and efficiency are paramount. They are ideal for applications requiring frequent tool changes, as they minimize the need for tool inventory and reduce setup times.
In summary, double-end end mills are versatile, cost-effective tools that enhance productivity and efficiency in milling operations by providing two cutting ends, thereby extending tool life and reducing operational costs.
How do double-end end mills differ from single-end end mills?
Double-end end mills have cutting edges on both ends of the tool, allowing them to be flipped and used again once one end becomes dull, effectively doubling the tool's lifespan. This design can be cost-effective as it reduces the need for frequent tool changes and inventory. However, double-end end mills are typically shorter in length compared to single-end end mills, which can limit their reach and depth of cut.
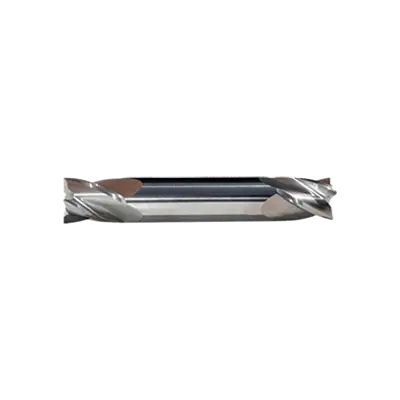
Single-end end mills, on the other hand, have cutting edges on only one end. They are generally longer, providing greater reach and flexibility in machining operations. This makes them suitable for deeper cuts and more complex machining tasks. Single-end end mills are often preferred for applications requiring longer tool reach or when working with materials that require more aggressive cutting.
In terms of tool holding, double-end end mills require a collet or tool holder that can accommodate the shank in the middle, while single-end end mills are held by the shank at the non-cutting end. This can affect the rigidity and stability of the tool during machining.
Overall, the choice between double-end and single-end end mills depends on the specific machining requirements, including the depth of cut, tool life considerations, and cost efficiency.
What materials can double-end end mills cut?
Double-end end mills can cut a variety of materials, including:
1. **Metals**:
- **Steel**: Suitable for cutting various types of steel, including carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel.
- **Aluminum**: Effective for machining aluminum and its alloys due to its softer nature.
- **Brass and Copper**: Can handle non-ferrous metals like brass and copper, which are softer and require less cutting force.
- **Cast Iron**: Capable of cutting cast iron, though tool wear may be higher due to the material's abrasive nature.
2. **Plastics**:
- **Acrylic and Polycarbonate**: Can cut through hard plastics like acrylic and polycarbonate with precision.
- **Nylon and Delrin**: Suitable for softer plastics such as nylon and Delrin, often used in engineering applications.
3. **Wood**:
- **Hardwood and Softwood**: Can be used for cutting both hardwoods and softwoods, though the tool geometry may need to be adjusted for optimal performance.
4. **Composites**:
- **Fiberglass and Carbon Fiber**: Can cut composite materials like fiberglass and carbon fiber, though care must be taken to minimize delamination and tool wear.
5. **Other Materials**:
- **Titanium**: With the right coatings and geometries, double-end end mills can cut titanium, though it requires careful control of cutting parameters.
- **Graphite**: Suitable for machining graphite, often used in EDM applications.
The choice of material that a double-end end mill can cut depends on the tool's material, coating, and geometry. Carbide end mills, for example, are more suitable for harder materials, while high-speed steel (HSS) end mills are often used for softer materials. Coatings like TiN, TiCN, or AlTiN can enhance performance by reducing wear and increasing heat resistance.
How do you choose the right double-end end mill for a project?
To choose the right double-end end mill for a project, consider the following factors:
1. **Material**: Match the end mill material to the workpiece material. Use high-speed steel (HSS) for softer materials and carbide for harder materials.
2. **Coating**: Select coatings like TiN, TiCN, or TiAlN to enhance tool life and performance, especially for high-speed applications or abrasive materials.
3. **Diameter and Length**: Choose the appropriate diameter for the desired cut width and ensure the length is sufficient for the depth of cut without causing deflection.
4. **Flute Count**: Use fewer flutes (2-3) for softer materials to allow better chip evacuation. Opt for more flutes (4 or more) for harder materials to improve finish and tool strength.
5. **Helix Angle**: A higher helix angle (40° or more) provides a smoother finish and is suitable for softer materials, while a lower angle (30° or less) is better for harder materials.
6. **End Geometry**: Select the end geometry based on the operation. Square ends are for flat-bottomed cuts, ball ends for contouring, and corner radius ends for increased strength and reduced chipping.
7. **Shank Type**: Ensure the shank type (straight or tapered) matches the machine's collet or holder for secure mounting.
8. **Machine Capability**: Consider the machine's spindle speed, power, and rigidity to ensure it can handle the chosen end mill without excessive wear or breakage.
9. **Cost and Availability**: Balance the cost with the expected tool life and availability to ensure timely project completion.
10. **Project Requirements**: Align the end mill choice with specific project needs, such as surface finish, tolerance, and production volume.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the most suitable double-end end mill for your project, optimizing performance and efficiency.
What are the advantages of using double-end end mills?
Double-end end mills offer several advantages:
1. **Cost-Effectiveness**: They provide two cutting ends, effectively doubling the tool life compared to single-end mills. This reduces the frequency of tool changes and the need for purchasing additional tools, leading to cost savings.
2. **Efficiency**: With two cutting ends, operators can quickly switch to a fresh cutting edge by simply flipping the tool, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
3. **Space-Saving**: Double-end mills require less storage space as they combine two tools into one, which is beneficial in environments with limited storage capacity.
4. **Versatility**: They are available in various sizes and shapes, suitable for a wide range of milling applications, including slotting, profiling, and contouring.
5. **Reduced Inventory**: Fewer tools are needed in inventory, simplifying tool management and reducing the complexity of tool selection.
6. **Environmental Impact**: By extending the tool life and reducing the need for frequent replacements, double-end mills contribute to less waste and a smaller environmental footprint.
7. **Convenience**: They are easy to handle and replace, as the same tool holder can be used for both ends, streamlining the tool change process.
8. **Durability**: Made from high-quality materials, they offer robust performance and can withstand demanding machining conditions.
Overall, double-end end mills are a practical choice for many machining operations, offering economic and operational benefits.
How do you maintain and store double-end end mills?
To maintain and store double-end end mills, follow these steps:
1. **Cleaning**: After each use, clean the end mills thoroughly to remove any debris, chips, or coolant. Use a soft brush or compressed air to ensure all particles are removed.
2. **Inspection**: Regularly inspect the end mills for wear, chipping, or damage. Check both cutting ends for sharpness and integrity. Replace or regrind if necessary.
3. **Lubrication**: Apply a light coat of rust-preventive oil to protect the end mills from corrosion, especially if they are made of high-speed steel.
4. **Proper Storage**: Store end mills in a dry, clean environment. Use dedicated storage solutions like end mill holders, racks, or cases that prevent contact between tools to avoid chipping or dulling.
5. **Labeling**: Clearly label storage containers with the size, type, and material of the end mills for easy identification and to prevent misuse.
6. **Environment Control**: Maintain a stable environment with controlled temperature and humidity to prevent rust and material degradation.
7. **Rotation**: Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system to ensure older tools are used before newer ones, preventing long-term storage issues.
8. **Sharpening**: Regularly sharpen end mills to maintain cutting efficiency. Use professional sharpening services or appropriate equipment to ensure precision.
9. **Training**: Ensure that all personnel handling the end mills are trained in proper handling and storage techniques to minimize damage and extend tool life.
10. **Documentation**: Keep records of usage, maintenance, and sharpening schedules to track the lifespan and performance of each end mill.
By following these practices, you can extend the life of double-end end mills and maintain their performance.
What are the common sizes and types of double-end end mills?
Double-end end mills are cutting tools used in milling applications, featuring cutting edges on both ends. This design allows for extended tool life, as both ends can be used before the tool needs replacement. Common sizes and types include:
1. **Sizes:**
- **Diameter:** Typically ranges from 1/8 inch to 1 inch, with metric sizes available from 3mm to 25mm.
- **Length:** Overall lengths vary, generally from 2 inches to 6 inches, depending on the diameter and application.
- **Shank Diameter:** Usually matches the cutting diameter, but can also be reduced for specific applications.
2. **Types:**
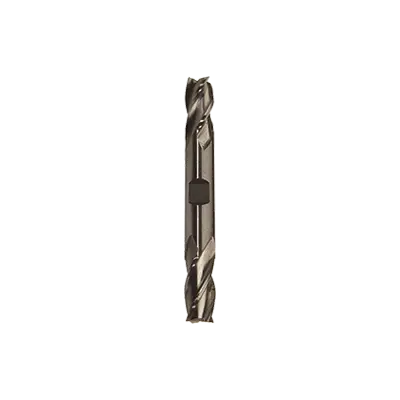
- **Square End Mills:** Feature a flat cutting edge, ideal for slotting, profiling, and plunge cutting.
- **Ball Nose End Mills:** Have a rounded cutting edge, suitable for 3D contouring and complex surface machining.
- **Corner Radius End Mills:** Combine features of square and ball nose end mills, with a small radius on the corners to improve strength and reduce chipping.
- **Roughing End Mills:** Designed with serrated cutting edges to remove large amounts of material quickly, often used in the initial stages of machining.
- **Finishing End Mills:** Provide a smooth surface finish, used after roughing operations.
3. **Materials:**
- **High-Speed Steel (HSS):** Offers good wear resistance and toughness, suitable for general-purpose milling.
- **Cobalt Steel:** Provides better heat resistance than HSS, ideal for harder materials.
- **Carbide:** Offers superior hardness and wear resistance, suitable for high-speed applications and hard materials.
4. **Coatings:**
- **TiN (Titanium Nitride):** Increases hardness and reduces friction.
- **TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride):** Offers better wear resistance than TiN.
- **AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride):** Provides excellent heat resistance, ideal for high-speed applications.
These variations allow double-end end mills to be versatile tools in various machining operations.