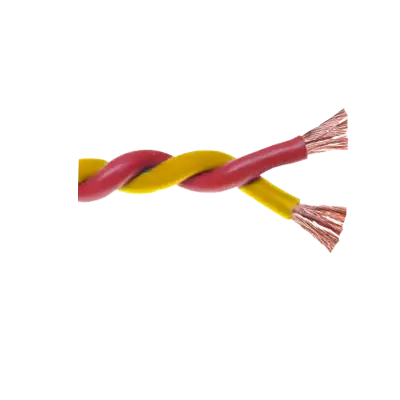Call +(254) 703 030 000 / 751 483 999 / 721 704 777
- Home
- Electrical
- Cables Conductors
- Copper Cables
- Blasting Wire
.....Read More
Frequently Asked Questions
What is blasting wire used for?
Blasting wire is used in the field of explosives and demolition to safely and effectively initiate and control the detonation of explosive charges. It serves as a critical component in the process of blasting, which is employed in various industries such as mining, construction, and quarrying. The primary function of blasting wire is to transmit an electrical signal from a safe distance to detonators or blasting caps, which then ignite the explosive material.
The wire is typically insulated to prevent accidental detonation and is designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions. It is laid out from the blasting site to a secure location where the blasting machine or control panel is operated. This allows operators to initiate the blast from a safe distance, minimizing the risk of injury or damage.
Blasting wire is available in different gauges and lengths, depending on the specific requirements of the blasting operation. It is often color-coded to help identify different circuits and ensure proper connections. The use of blasting wire is crucial for synchronizing multiple charges, allowing for precise control over the timing and sequence of explosions. This precision is essential for achieving the desired fragmentation of rock or other materials, optimizing the efficiency of the operation, and ensuring safety.
In summary, blasting wire is an essential tool in the controlled use of explosives, providing a reliable means of transmitting the necessary electrical signals to initiate detonations safely and effectively.
How does blasting wire work?
Blasting wire is used in the process of detonating explosives, typically in mining, construction, and demolition. It serves as a conduit for transmitting an electrical signal from a power source to an explosive device, such as a detonator or blasting cap. Here's how it works:
1. **Material and Construction**: Blasting wire is usually made of copper or aluminum, chosen for their excellent conductivity. It is insulated with materials like PVC or polyethylene to prevent short circuits and protect against environmental factors.
2. **Connection**: The blasting wire is connected to an electric detonator, which is embedded in the explosive material. The other end of the wire is connected to a blasting machine or power source, which generates the necessary electrical current.
3. **Signal Transmission**: When the blasting machine is activated, it sends an electrical current through the blasting wire. This current travels along the wire to the detonator.
4. **Detonation**: The electrical current heats a bridge wire or a small resistor inside the detonator, igniting a pyrotechnic compound. This ignition sets off a primary explosive within the detonator, which in turn detonates the main explosive charge.
5. **Safety and Control**: Blasting wire allows for precise control over the timing and sequence of detonations. By varying the length and configuration of the wire, multiple charges can be detonated in a specific order, optimizing the effectiveness of the blast and enhancing safety.
6. **Durability and Reliability**: The wire must be durable enough to withstand harsh conditions, such as moisture, abrasion, and temperature extremes, ensuring reliable performance during blasting operations.
In summary, blasting wire is a critical component in controlled detonation, providing a safe and efficient means to initiate explosive charges through electrical signals.
What are the safety precautions for using blasting wire?
1. **Inspection**: Regularly inspect blasting wire for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion. Replace any compromised sections immediately.
2. **Storage**: Store blasting wire in a dry, cool, and secure location away from any potential sources of damage or contamination.
3. **Handling**: Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses when handling blasting wire to prevent injuries.
4. **Routing**: Ensure the wire is routed away from sharp edges, heavy machinery, and high-traffic areas to prevent accidental cuts or crushing.
5. **Connections**: Securely connect blasting wire to detonators and ensure all connections are tight and free from any loose strands that could cause a short circuit.
6. **Distance**: Maintain a safe distance from the blast site when laying and connecting blasting wire to minimize exposure to potential hazards.
7. **Grounding**: Ensure proper grounding of the blasting circuit to prevent accidental initiation from static electricity or stray currents.
8. **Testing**: Use a blasting galvanometer to test the continuity and resistance of the blasting circuit before connecting to the power source.
9. **Isolation**: Keep blasting wire isolated from other electrical circuits and power sources to prevent accidental initiation.
10. **Communication**: Maintain clear communication with all personnel involved in the blasting operation to ensure everyone is aware of the status and location of the blasting wire.
11. **Training**: Ensure all personnel handling blasting wire are adequately trained in its use and the associated safety protocols.
12. **Regulations**: Adhere to all relevant regulations and guidelines set by authorities regarding the use and handling of blasting wire.
13. **Emergency Procedures**: Have clear emergency procedures in place in case of accidental initiation or other incidents involving blasting wire.
What materials are blasting wires made from?
Blasting wires, also known as detonator wires or firing lines, are typically made from materials that ensure durability, conductivity, and safety in explosive environments. The primary materials used in the construction of blasting wires include:
1. **Copper**: Copper is a common choice for the conductive core of blasting wires due to its excellent electrical conductivity, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion. It ensures efficient transmission of the electrical signal required to initiate the detonator.
2. **Aluminum**: Aluminum is another material used for the conductive core. It is lighter and less expensive than copper, making it a cost-effective alternative. However, it has slightly lower conductivity compared to copper.
3. **Steel**: In some cases, steel wires are used, especially in environments where additional strength and durability are required. Steel is less conductive than copper and aluminum but offers greater tensile strength.
4. **Insulation Materials**: The conductive core is typically insulated with materials such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride), polyethylene, or rubber. These materials provide electrical insulation, protect against environmental factors like moisture and abrasion, and enhance safety by preventing accidental short circuits.
5. **Jacket Materials**: The outer jacket of blasting wires is often made from durable, weather-resistant materials like polyethylene or PVC. This outer layer provides additional protection against physical damage and environmental exposure.
Blasting wires are designed to withstand harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures, moisture, and mechanical stress, ensuring reliable performance in mining, construction, and demolition applications. The choice of materials depends on factors such as cost, environmental conditions, and specific application requirements.
How do you choose the right blasting wire for a project?
To choose the right blasting wire for a project, consider the following factors:
1. **Type of Blasting**: Determine whether the project involves surface or underground blasting, as this affects the wire's durability and insulation requirements.
2. **Wire Material**: Choose between copper or aluminum wires. Copper offers better conductivity and flexibility, while aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective.
3. **Insulation**: Select appropriate insulation based on environmental conditions. PVC is common for general use, while polyethylene or rubber is better for wet or harsh conditions.
4. **Wire Gauge**: Consider the distance between the blasting machine and the detonators. Longer distances require thicker wires to minimize resistance and ensure reliable current flow.
5. **Resistance to Environmental Conditions**: Ensure the wire can withstand the specific environmental conditions of the site, such as temperature extremes, moisture, and chemical exposure.
6. **Safety Standards**: Ensure compliance with industry safety standards and regulations, such as those from the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) or Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
7. **Cost**: Balance cost with performance requirements. Higher-quality wires may have a higher upfront cost but can offer better reliability and safety.
8. **Supplier Reputation**: Choose wires from reputable suppliers known for quality and reliability to minimize the risk of failure.
9. **Project Scale**: For large-scale projects, consider the logistics of wire deployment and retrieval, ensuring the wire length and spool size are manageable.
10. **Compatibility**: Ensure the wire is compatible with the blasting equipment and detonators being used.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the most suitable blasting wire for your specific project needs.
What are the environmental considerations for using blasting wire?
Environmental considerations for using blasting wire include:
1. **Material Composition**: Blasting wires are often made from metals and plastics, which can contribute to environmental pollution if not disposed of properly. The degradation of these materials can release harmful substances into the soil and water.
2. **Waste Management**: Improper disposal of blasting wire can lead to littering and environmental contamination. Effective waste management practices are necessary to ensure that used wires are collected and recycled or disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner.
3. **Habitat Disruption**: The use of blasting wire is typically associated with mining and construction activities, which can disrupt local ecosystems and wildlife habitats. Careful planning is required to minimize the impact on flora and fauna.
4. **Noise Pollution**: The use of blasting wire in detonations contributes to noise pollution, which can affect both human populations and wildlife. Measures should be taken to mitigate noise levels, especially in sensitive areas.
5. **Chemical Residues**: Blasting operations can leave behind chemical residues that may leach into the environment. It is important to monitor and manage these residues to prevent soil and water contamination.
6. **Energy Consumption**: The production and transportation of blasting wire consume energy, contributing to carbon emissions. Opting for more sustainable materials and local sourcing can help reduce the carbon footprint.
7. **Regulatory Compliance**: Adhering to environmental regulations and standards is crucial to minimize the ecological impact. This includes obtaining necessary permits and conducting environmental impact assessments.
8. **Rehabilitation Efforts**: Post-blasting site rehabilitation is essential to restore the environment. This involves replanting vegetation, restoring habitats, and ensuring that the area is safe for wildlife and human use.
9. **Community Impact**: Consideration of the social and environmental impact on local communities is important. Engaging with stakeholders and addressing their concerns can lead to more sustainable practices.
How do you properly store and handle blasting wire?
To properly store and handle blasting wire, follow these guidelines:
1. **Storage Conditions**: Keep blasting wire in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, moisture, and extreme temperatures to prevent degradation.
2. **Segregation**: Store blasting wire separately from other explosives and flammable materials to minimize risk. Use designated storage areas or containers specifically for blasting materials.
3. **Labeling**: Clearly label all storage containers with the contents and relevant safety information. Ensure that labels are visible and legible.
4. **Inventory Management**: Maintain an accurate inventory of blasting wire, including batch numbers and expiration dates. Regularly inspect stock to ensure it is within its usable life.
5. **Handling Procedures**: Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses when handling blasting wire. Follow all safety protocols and manufacturer instructions.
6. **Transportation**: Transport blasting wire in approved containers, ensuring it is secure and protected from physical damage. Use vehicles that comply with regulations for transporting hazardous materials.
7. **Training**: Ensure all personnel handling blasting wire are trained in proper handling techniques and emergency procedures. Conduct regular safety drills and refreshers.
8. **Inspection**: Regularly inspect blasting wire for signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Discard any compromised wire according to safety guidelines.
9. **Documentation**: Keep detailed records of all handling, storage, and disposal activities. Ensure compliance with local, state, and federal regulations.
10. **Emergency Preparedness**: Have an emergency response plan in place, including procedures for dealing with accidental ignition or exposure. Ensure all personnel are familiar with the plan.
By adhering to these practices, you can ensure the safe and effective storage and handling of blasting wire.