Call +(254) 703 030 000 / 751 483 999 / 721 704 777
- Home
- Raw Materials
- Metals
- Carbon Steel
- Carbon Steel Sheets Plates
.....Read More
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different grades of carbon steel sheets and plates?
Carbon steel sheets and plates are categorized based on their carbon content and other alloying elements, which affect their mechanical properties and applications. The main grades include:
1. **Low Carbon Steel (Mild Steel):** Contains approximately 0.05% to 0.25% carbon. It is highly ductile, malleable, and easy to weld, making it suitable for applications like automotive panels, structural shapes, and pipes.
2. **Medium Carbon Steel:** Contains about 0.25% to 0.60% carbon. It offers a balance between strength and ductility, making it ideal for manufacturing gears, axles, and other mechanical components.
3. **High Carbon Steel:** Contains 0.60% to 1.0% carbon. It is very strong and hard but less ductile, used in high-strength applications like cutting tools, springs, and high-strength wires.
4. **Ultra-High Carbon Steel:** Contains 1.0% to 2.0% carbon. It is extremely hard and brittle, used in specialized applications like knives, axles, and punches.
5. **Alloy Carbon Steel:** Contains additional alloying elements like manganese, silicon, and copper to enhance properties like strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. Common grades include A36, A572, and A588.
6. **Tool Steel:** A subset of high carbon steel, it includes elements like tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium to improve hardness and heat resistance, used in cutting and shaping tools.
7. **Spring Steel:** Known for its high yield strength, it is used in the manufacture of springs and high-stress applications.
Each grade is selected based on the specific requirements of the application, considering factors like tensile strength, ductility, weldability, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
How do textured carbon steel plates improve traction?
Textured carbon steel plates improve traction by increasing the surface roughness, which enhances the frictional force between the plate and any object in contact with it. The texture, often in the form of raised patterns such as diamonds, teardrops, or other geometric shapes, provides multiple contact points and edges. These features disrupt the smoothness of the surface, allowing for better grip and reducing the likelihood of slipping.
The increased friction is due to both mechanical interlocking and the increased surface area provided by the texture. Mechanical interlocking occurs when the raised patterns on the steel plate physically engage with the surface of the contacting object, such as a shoe sole or a vehicle tire. This engagement helps resist lateral movement, thereby improving stability and traction.
Additionally, the texture helps in channeling away substances like water, oil, or debris that might otherwise reduce friction. By providing pathways for these substances to escape, the textured surface maintains better contact with the object, further enhancing traction.
Textured carbon steel plates are also durable and resistant to wear, maintaining their traction-enhancing properties over time. This makes them suitable for high-traffic areas or environments where safety is a concern, such as industrial floors, stair treads, and ramps.
In summary, textured carbon steel plates improve traction by increasing friction through mechanical interlocking, enhancing surface area, and effectively managing contaminants that could reduce grip.
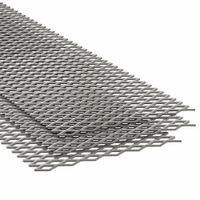
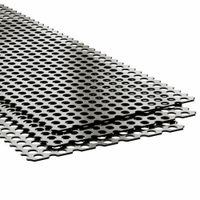
What are the applications of expanded carbon steel sheets?
Expanded carbon steel sheets have a wide range of applications due to their strength, durability, and versatility. They are commonly used in:
1. **Construction and Architecture**: Used for walkways, platforms, and stair treads due to their non-slip surface. They also serve as decorative elements in facades and partitions.
2. **Industrial and Manufacturing**: Employed in machinery guards, enclosures, and as support for heavy equipment. Their open structure allows for ventilation and drainage.
3. **Automotive Industry**: Utilized in the production of grilles, filters, and reinforcement components due to their lightweight yet strong nature.
4. **Security and Safety**: Used in fencing, barriers, and security screens to provide protection while maintaining visibility and airflow.
5. **Agriculture**: Applied in flooring for animal enclosures and as support for plants in greenhouses due to their durability and ease of cleaning.
6. **Energy Sector**: Used in oil and gas platforms, and as support structures in renewable energy installations like solar panels.
7. **Transportation**: Employed in the construction of trailers, truck beds, and railway cars for their strength and ability to withstand heavy loads.
8. **Filtration**: Used in filters and strainers in various industries due to their ability to allow passage of air or liquids while blocking larger particles.
9. **Marine Applications**: Suitable for use in shipbuilding and offshore platforms due to their resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
10. **Art and Design**: Used by artists and designers for sculptures and installations due to their unique texture and appearance.
These applications leverage the material's properties such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion, making expanded carbon steel sheets a valuable resource across multiple industries.
How is the durability of carbon steel sheets and plates measured?
The durability of carbon steel sheets and plates is measured through several key parameters and tests:
1. **Tensile Strength**: This measures the maximum stress that carbon steel can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. It indicates the material's ability to resist deformation and failure under load.
2. **Yield Strength**: This is the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically. Beyond this point, the material will deform permanently. It is crucial for determining the load that the steel can handle without permanent deformation.
3. **Hardness Tests**: Methods like Rockwell, Brinell, or Vickers hardness tests are used to measure the resistance of carbon steel to indentation. Hardness is directly related to wear resistance and durability.
4. **Impact Resistance**: The Charpy or Izod impact tests measure the material's ability to absorb energy during a high-strain rate event, such as a blow or sudden impact. This is crucial for applications where the steel might experience sudden forces.
5. **Corrosion Resistance**: Although carbon steel is not inherently corrosion-resistant, its durability in corrosive environments can be assessed through salt spray tests or exposure to specific environments to measure the rate of corrosion.
6. **Fatigue Strength**: This measures the material's ability to withstand repeated loading and unloading cycles. It is essential for applications where the steel will experience fluctuating stresses.
7. **Thickness and Coating**: The thickness of the steel and any protective coatings (like galvanization) can also affect durability by providing additional resistance to wear and corrosion.
8. **Microstructural Analysis**: Examining the grain structure and phase distribution through microscopy can provide insights into the material's toughness and potential weak points.
These tests and analyses collectively provide a comprehensive understanding of the durability of carbon steel sheets and plates, ensuring they meet the required performance standards for their intended applications.
What are the benefits of using perforated carbon steel sheets?
Perforated carbon steel sheets offer several benefits:
1. **Strength and Durability**: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and durability, making these sheets suitable for heavy-duty applications.
2. **Versatility**: They can be used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing, due to their adaptability in different environments.
3. **Aesthetic Appeal**: The perforations can be customized in various patterns, enhancing the visual appeal for architectural applications.
4. **Weight Reduction**: The perforations reduce the overall weight of the sheets without compromising structural integrity, making them easier to handle and install.
5. **Ventilation and Airflow**: The holes allow for excellent ventilation and airflow, which is beneficial in HVAC systems and other applications requiring air circulation.
6. **Sound Absorption**: They can be used in acoustic applications to reduce noise levels by absorbing sound waves.
7. **Cost-Effectiveness**: Carbon steel is generally more affordable than other metals, providing a cost-effective solution for projects requiring large quantities of material.
8. **Corrosion Resistance**: When properly coated or treated, carbon steel sheets can resist corrosion, extending their lifespan in various environments.
9. **Filtration**: The perforations can serve as a filtering medium in industrial processes, allowing for the separation of solids from liquids or gases.
10. **Safety and Security**: They can be used as protective barriers or enclosures, providing security while maintaining visibility and airflow.
11. **Ease of Fabrication**: Carbon steel sheets are easy to cut, bend, and weld, allowing for customization and ease of installation.
12. **Recyclability**: Being made of steel, they are fully recyclable, contributing to environmental sustainability.
How do you choose the right carbon steel grade for a specific application?
To choose the right carbon steel grade for a specific application, consider the following factors:
1. **Mechanical Properties**: Determine the required strength, ductility, and hardness. Low carbon steels (e.g., AISI 1010) offer good ductility and are easy to form, while high carbon steels (e.g., AISI 1095) provide higher strength and hardness.
2. **Weldability**: Low carbon steels are generally more weldable. If welding is a key process, opt for grades with lower carbon content to minimize the risk of cracking.
3. **Machinability**: Consider the ease of machining. Medium carbon steels (e.g., AISI 1045) offer a balance between machinability and strength, suitable for parts requiring moderate strength and good machinability.
4. **Corrosion Resistance**: Carbon steels are not inherently corrosion-resistant. For applications exposed to moisture or corrosive environments, consider coatings or alternative materials unless the application allows for regular maintenance.
5. **Heat Treatment**: Determine if the application requires heat treatment for enhanced properties. High carbon steels can be heat-treated for increased hardness and strength.
6. **Cost**: Balance performance requirements with budget constraints. Low carbon steels are generally more cost-effective, while high carbon steels may incur additional costs due to heat treatment and machining.
7. **Application Environment**: Consider the operating environment, including temperature and exposure to chemicals. High carbon steels may become brittle at low temperatures, while low carbon steels may not perform well at high temperatures.
8. **Standards and Specifications**: Adhere to industry standards and specifications (e.g., ASTM, SAE) relevant to the application to ensure compliance and performance.
By evaluating these factors, you can select a carbon steel grade that meets the specific requirements of your application, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
What is the difference between standard and textured carbon steel plates?
Standard carbon steel plates are flat sheets of steel with a uniform surface, typically used in applications where a smooth finish is required. They are produced through a process of rolling and are available in various thicknesses and grades, depending on the carbon content and other alloying elements. These plates are commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and structural applications due to their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Textured carbon steel plates, on the other hand, have a patterned surface, which can be achieved through embossing or rolling with patterned rollers. The texture can vary from simple patterns like diamond or teardrop to more complex designs. The primary purpose of texturing is to enhance the plate's grip and slip resistance, making them ideal for flooring, stair treads, and other applications where traction is important. Textured plates can also be used for aesthetic purposes, providing a decorative finish in architectural applications.
The key differences between the two lie in their surface finish and intended applications. Standard plates are chosen for their smoothness and are often used where a flat, even surface is necessary. Textured plates are selected for their enhanced grip and visual appeal. Additionally, the manufacturing process for textured plates may involve additional steps to create the desired pattern, potentially affecting cost and availability compared to standard plates.