Call +(254) 703 030 000 / 751 483 999 / 721 704 777
- Home
- Material Handling
- Transporting
- Conveyors Components
- Skate Wheel Conveyors Components
.....Read More
Frequently Asked Questions
What are skate wheel conveyors used for?
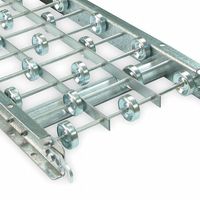
Skate wheel conveyors are used for the efficient and cost-effective movement of lightweight packages, cartons, and other flat-bottomed items in various industrial and commercial settings. They consist of a series of small, individual wheels mounted on a frame, allowing items to glide smoothly over the surface with minimal manual effort. These conveyors are particularly advantageous in environments where flexibility and portability are essential, as they are often lightweight and easy to reconfigure or relocate.
Common applications include assembly lines, packaging stations, and shipping areas, where they facilitate the quick transfer of goods between workstations or to and from storage areas. They are also frequently used in retail settings for restocking shelves or moving products from the backroom to the sales floor. In distribution centers and warehouses, skate wheel conveyors help streamline the order fulfillment process by enabling the rapid movement of goods along picking lines.
Skate wheel conveyors are ideal for gravity flow systems, where the natural force of gravity assists in moving items along a slightly inclined path, reducing the need for powered systems. This makes them energy-efficient and cost-effective, as they require no electricity or complex machinery to operate. Additionally, they are often modular, allowing for easy customization to fit specific spatial requirements or to accommodate changes in workflow.
Overall, skate wheel conveyors are a versatile and practical solution for enhancing productivity and efficiency in environments that handle lightweight, uniform items, providing a simple yet effective means of material handling.
How do skate wheel conveyors work?
Skate wheel conveyors are a type of gravity conveyor that use a series of small, free-spinning wheels mounted on axles to facilitate the movement of items. These wheels are typically made of materials like steel, aluminum, or plastic and are arranged in rows along the conveyor frame. The frame itself is usually constructed from metal or durable plastic, providing a sturdy base for the wheels.
The operation of skate wheel conveyors relies on gravity and the natural inclination of the conveyor. They are often set at a slight downward angle, allowing items placed on the conveyor to move forward under their own weight. The wheels reduce friction, enabling smooth and easy movement of items with minimal manual effort.
Items are placed on the conveyor, and as they move, the wheels rotate, allowing the items to glide along the conveyor path. The spacing and size of the wheels can be adjusted to accommodate different types of loads, making skate wheel conveyors versatile for various applications. They are particularly effective for handling lightweight, flat-bottomed items such as boxes, trays, and cartons.
Skate wheel conveyors are commonly used in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities for tasks like loading, unloading, and sorting. They are also popular in retail environments for moving products from storage areas to sales floors. Their modular design allows for easy customization and reconfiguration to fit specific layout requirements.
Overall, skate wheel conveyors offer a cost-effective, low-maintenance solution for material handling, providing efficient and flexible transport of goods without the need for powered systems.
What are the advantages of using skate wheel conveyors?
Skate wheel conveyors offer several advantages:
1. **Cost-Effectiveness**: They are generally less expensive than powered conveyors, making them a budget-friendly option for many businesses.
2. **Flexibility**: These conveyors are lightweight and portable, allowing for easy reconfiguration and relocation to suit changing operational needs.
3. **Ease of Installation**: Skate wheel conveyors are simple to set up and require minimal tools and expertise, reducing installation time and costs.
4. **Low Maintenance**: With fewer moving parts compared to powered systems, they require less maintenance, leading to lower long-term operational costs.
5. **Energy Efficiency**: As they rely on gravity or manual force, they do not consume electricity, making them an environmentally friendly option.
6. **Versatility**: Suitable for handling a wide range of products, including boxes, totes, and other flat-bottomed items, they are ideal for various industries.
7. **Space-Saving**: Their compact design allows for efficient use of space, which is beneficial in areas with limited room.
8. **Scalability**: Easily expandable by adding more sections, they can grow with the business without significant investment.
9. **Safety**: With no electrical components, they pose fewer safety risks, reducing the likelihood of accidents related to electrical malfunctions.
10. **Smooth Product Flow**: The design allows for smooth and consistent movement of products, minimizing the risk of damage during transit.
11. **Customizability**: Available in various widths and lengths, they can be tailored to specific operational requirements.
12. **Minimal Training Required**: Simple operation means that employees require little training to use them effectively, enhancing productivity.
These advantages make skate wheel conveyors a practical choice for many material handling applications.
How do you install skate wheel conveyors?
1. **Site Preparation**: Clear the installation area of any obstructions and ensure the floor is level and clean.
2. **Layout Planning**: Measure the area where the conveyor will be installed. Plan the path, considering the start and end points, and any curves or inclines.
3. **Unpack Components**: Unpack all conveyor components, including frames, skate wheels, axles, and supports. Check for any damage and ensure all parts are present.
4. **Assemble Frames**: Connect the conveyor frames according to the manufacturer's instructions. Use bolts and nuts to secure the sections together.
5. **Install Supports**: Position the conveyor supports at regular intervals along the planned path. Adjust the height of the supports to ensure the conveyor is level or inclined as needed.
6. **Attach Skate Wheels**: Insert axles into the pre-drilled holes on the conveyor frames. Slide skate wheels onto the axles, ensuring they are evenly spaced. Secure the wheels with axle clips or nuts.
7. **Connect Sections**: If the conveyor consists of multiple sections, connect them using the provided connectors or brackets. Ensure the transitions between sections are smooth.
8. **Secure the Conveyor**: Anchor the conveyor supports to the floor if necessary, especially in high-traffic areas or where stability is a concern.
9. **Test the Conveyor**: Run a few test items through the conveyor to check for smooth operation. Adjust the height or alignment of the supports if needed.
10. **Final Adjustments**: Make any final adjustments to ensure optimal performance. Tighten all bolts and nuts to prevent loosening during operation.
11. **Safety Check**: Ensure all safety features are in place, such as guardrails or end stops, to prevent items from falling off the conveyor.
What materials are skate wheel conveyors made from?
Skate wheel conveyors are typically constructed from a combination of materials to ensure durability, functionality, and cost-effectiveness. The primary materials used include:
1. **Steel**: Steel is commonly used for the frame and the axles of skate wheel conveyors due to its strength and durability. It can withstand heavy loads and is resistant to wear and tear, making it ideal for industrial environments.
2. **Aluminum**: Aluminum is often used for the frame in lighter-duty applications. It is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and easy to handle, making it suitable for portable or temporary conveyor setups.
3. **Plastic**: The wheels themselves are frequently made from high-impact plastic materials such as polypropylene or polyethylene. These plastics are chosen for their lightweight properties, resistance to corrosion, and ability to reduce noise during operation. They are also cost-effective and can handle a variety of environmental conditions.
4. **Stainless Steel**: In environments where hygiene is crucial, such as food processing or pharmaceuticals, stainless steel may be used for both the frame and the wheels. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and is easy to clean, ensuring compliance with health and safety standards.
5. **Zinc-Plated Steel**: For added corrosion resistance, especially in outdoor or humid environments, zinc-plated steel may be used for the frame and axles. The zinc coating provides a protective layer that helps prevent rust.
6. **Rubber or Urethane Coatings**: Some skate wheels may have a rubber or urethane coating to enhance grip and reduce noise. These coatings can also help protect delicate items being conveyed.
These materials are selected based on the specific requirements of the application, including load capacity, environmental conditions, and cost considerations.
How do you maintain skate wheel conveyors?
To maintain skate wheel conveyors, follow these steps:
1. **Regular Inspection**: Conduct routine checks for any visible damage or wear on the wheels, axles, and frames. Look for misalignment, bent frames, or broken wheels.
2. **Cleaning**: Keep the conveyor clean by removing debris, dust, and any material build-up. Use a soft brush or compressed air to clean the wheels and frames.
3. **Lubrication**: Apply a suitable lubricant to the wheel bearings and axles to ensure smooth operation. Avoid over-lubrication, which can attract dust and debris.
4. **Alignment**: Ensure that the conveyor is properly aligned. Misalignment can cause uneven wear on the wheels and affect the conveyor's efficiency.
5. **Wheel Replacement**: Replace any damaged or excessively worn wheels immediately to prevent further damage and maintain smooth operation.
6. **Frame Maintenance**: Check the frame for any signs of rust or corrosion. Apply a rust inhibitor or paint to protect the metal surfaces.
7. **Fasteners Check**: Tighten any loose bolts, nuts, or screws to ensure the conveyor remains stable and secure during operation.
8. **Load Capacity**: Ensure that the conveyor is not overloaded. Adhere to the manufacturer's specified load capacity to prevent damage to the wheels and frame.
9. **Training**: Train personnel on proper loading techniques and the importance of regular maintenance to prolong the conveyor's lifespan.
10. **Documentation**: Keep a maintenance log to track inspections, repairs, and replacements. This helps in identifying recurring issues and planning preventive maintenance.
By following these steps, you can ensure the efficient and long-lasting operation of skate wheel conveyors.
Can skate wheel conveyors handle heavy loads?
Skate wheel conveyors are generally not designed to handle heavy loads. They are best suited for lightweight to medium-weight items. The design of skate wheel conveyors involves a series of small, individual wheels mounted on a frame, which allows for easy movement of items with minimal friction. This makes them ideal for transporting boxes, packages, and other items that are not excessively heavy.
The limitations in handling heavy loads stem from several factors:
1. **Wheel Material and Size**: The wheels are typically made from plastic or light metal, which may not withstand the stress of heavy loads. Larger and heavier items can cause the wheels to deform or break.
2. **Frame Structure**: The frame of a skate wheel conveyor is usually lightweight to facilitate easy movement and installation. This structure may not provide the necessary support for heavy items, leading to potential bending or collapse.
3. **Load Distribution**: Heavy loads can cause uneven distribution of weight across the wheels, leading to increased wear and potential failure of the conveyor system.
4. **Friction and Movement**: While skate wheel conveyors are designed for low friction, heavy loads can increase friction significantly, making it difficult to move items smoothly and potentially causing damage to the wheels and frame.
For applications involving heavy loads, other types of conveyors, such as roller conveyors or belt conveyors, are more appropriate. These systems are specifically designed to handle greater weights, with stronger materials and more robust construction to ensure durability and reliability.