Call +(254) 703 030 000 / 751 483 999 / 721 704 777
- Home
- Material Handling
- Transporting
- Conveyors Components
- Material Flow Racks Rails
.....Read More
Frequently Asked Questions
What are material flow racks and rails?
Material flow racks and rails are systems designed to facilitate the efficient movement, storage, and organization of materials within a warehouse or manufacturing environment.
Material flow racks, often referred to as flow racks or gravity flow racks, are storage systems that use gravity to move items from the back to the front of the rack. They are typically inclined and equipped with rollers or wheels, allowing items to slide forward as they are removed from the front. This design supports first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory management, ensuring that older stock is used before newer stock. Flow racks are commonly used for high-volume, fast-moving products and are ideal for environments where quick access to inventory is crucial.
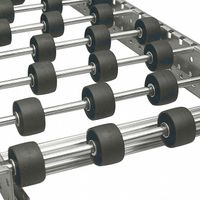
Material flow rails, on the other hand, are components used within these systems to guide and support the movement of items. They can be integrated into flow racks or used independently in various material handling applications. Rails are often made of durable materials like steel or aluminum and can be equipped with rollers or wheels to facilitate smooth movement. They are used to direct the flow of materials along a predetermined path, ensuring efficient and organized transport.
Both material flow racks and rails are essential for optimizing space, improving workflow efficiency, and reducing handling time in industrial settings. They help minimize labor costs, enhance safety by reducing clutter, and improve inventory management by providing clear visibility and easy access to stored items. These systems are customizable to fit specific operational needs, making them versatile solutions for various industries, including automotive, retail, and food and beverage.
How do flow rack conveyors work?
Flow rack conveyors, also known as gravity flow racks or carton flow racks, operate using a system of inclined shelves equipped with rollers or wheels. These conveyors are designed to facilitate the movement of goods from the back to the front of the storage system, utilizing gravity to assist in the process.
The system is structured with a series of lanes, each containing a set of rollers or wheels that are slightly inclined. When items, typically cartons or totes, are placed at the higher end of the lane, gravity causes them to roll down to the lower end, where they are easily accessible for picking. This design supports a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory management system, ensuring that older stock is used before newer stock.
Flow rack conveyors are particularly beneficial in environments where high-density storage and efficient picking are required, such as in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities. They help in reducing the time and effort needed for order picking, as items are automatically brought to the front of the rack, minimizing the need for workers to reach or travel long distances.
The system can be customized to accommodate various sizes and types of products by adjusting the width of the lanes and the type of rollers or wheels used. Additionally, flow rack conveyors can be integrated with other material handling systems, such as automated picking systems, to further enhance efficiency.
Overall, flow rack conveyors offer a cost-effective and efficient solution for managing inventory and improving the speed and accuracy of order fulfillment processes.
What are the benefits of using flow rails in inventory management?
Flow rails in inventory management offer several benefits:
1. **Improved Organization**: Flow rails facilitate a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system, ensuring older stock is used first, reducing waste and spoilage.
2. **Increased Efficiency**: They streamline the picking process by automatically moving products to the front, reducing the time and effort needed to retrieve items.
3. **Space Optimization**: By utilizing gravity, flow rails allow for denser storage, maximizing warehouse space and reducing the need for additional storage facilities.
4. **Reduced Labor Costs**: With products automatically moving forward, less manual handling is required, decreasing labor costs and minimizing the risk of injury.
5. **Enhanced Inventory Control**: Flow rails provide better visibility and access to inventory, making it easier to monitor stock levels and reduce overstocking or stockouts.
6. **Scalability**: They can be easily adjusted or expanded to accommodate changes in inventory size or product lines, offering flexibility in dynamic business environments.
7. **Improved Accuracy**: By organizing products systematically, flow rails reduce picking errors, enhancing order accuracy and customer satisfaction.
8. **Reduced Damage**: The controlled movement of products minimizes handling, reducing the risk of damage during storage and retrieval.
9. **Cost-Effective**: While the initial investment may be significant, the long-term savings in labor, space, and inventory management often outweigh the costs.
10. **Sustainability**: By reducing waste and optimizing space, flow rails contribute to more sustainable inventory practices.
Overall, flow rails enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of inventory management systems.
How are flow rails installed onto pallet racks?
Flow rails are installed onto pallet racks through a series of steps designed to ensure stability and functionality. First, assess the pallet rack structure to determine the appropriate size and type of flow rails needed, considering the weight and dimensions of the items to be stored.
Next, prepare the pallet rack by ensuring it is level and securely anchored to the floor. This is crucial for the safe operation of flow rails.
Then, attach the flow rails to the beams of the pallet rack. This is typically done using brackets or clips that are specifically designed for the flow rail system being used. The rails should be installed at a slight incline, usually between 3 to 5 degrees, to allow gravity to facilitate the movement of items from the loading end to the picking end.
Ensure that the rails are aligned properly and securely fastened to prevent any movement or misalignment during use. It is important to check that the rails are parallel and evenly spaced to accommodate the pallets or cartons that will be placed on them.
Once installed, test the flow rails by placing a pallet or carton on the loading end and observing its movement to the picking end. Adjust the incline or alignment if necessary to ensure smooth operation.
Finally, conduct a safety check to ensure that all components are securely fastened and that there are no obstructions or potential hazards. Regular maintenance and inspections should be scheduled to ensure the continued safe and efficient operation of the flow rails.
What is the difference between flow racks and flow rails?
Flow racks and flow rails are both used in material handling and storage systems, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
Flow Racks:
- Flow racks are complete storage systems designed to facilitate the first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory management method.
- They consist of inclined shelves or lanes equipped with rollers or wheels, allowing products to move from the loading side to the picking side by gravity.
- Flow racks are typically used in warehouses and distribution centers for high-density storage and efficient order picking.
- They are ideal for environments with high product turnover and are often used for storing cartons, bins, or pallets.
- Flow racks can be customized with various accessories like dividers, guides, and braking systems to accommodate different product types and sizes.
Flow Rails:
- Flow rails are components used within flow racks or other storage systems to facilitate the movement of products.
- They consist of a series of rollers or wheels mounted on a rail, allowing items to glide smoothly along the track.
- Flow rails can be installed in existing shelving or racking systems to convert them into gravity-fed systems.
- They are versatile and can be used for various applications, including carton flow, pallet flow, and even in assembly lines.
- Flow rails are often used in situations where a full flow rack system is not necessary or feasible, providing a cost-effective solution for enhancing product movement.
In summary, flow racks are complete systems designed for efficient storage and retrieval, while flow rails are components that enable product movement within these systems or other setups.
How do flow racks support FIFO inventory management?
Flow racks support FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory management by utilizing a gravity-fed system that ensures the oldest inventory is used first. These racks are designed with a slight incline, allowing products to move forward automatically as items in the front are removed. This setup ensures that the first items placed on the rack are the first to be picked, maintaining the FIFO principle.
The design of flow racks typically includes rollers or wheels that facilitate the smooth movement of products from the back to the front. When a product is picked from the front, the next item in line rolls forward to take its place. This continuous flow minimizes handling and reduces the risk of stock obsolescence, spoilage, or expiration, which is particularly beneficial for perishable goods or items with a limited shelf life.
Flow racks also enhance inventory visibility and accessibility, making it easier for workers to identify and pick the correct items. This reduces picking errors and improves overall efficiency in the warehouse or storage facility. By maintaining a consistent flow of inventory, flow racks help in optimizing space utilization and reducing the need for excessive manual handling, which can lead to damage or misplacement of products.
Additionally, flow racks can be integrated into automated systems, further streamlining the inventory management process. This integration can include sensors and tracking systems that monitor inventory levels and movement, providing real-time data for better inventory control and planning.
Overall, flow racks are an effective tool for supporting FIFO inventory management by ensuring a systematic and efficient flow of products, reducing waste, and improving operational efficiency.
What types of items can be used with flow rack conveyors and rails?
Flow rack conveyors and rails are designed to handle a variety of items, primarily those that are uniform in size and shape to ensure smooth movement. Common items include:
1. **Cartons and Boxes**: These are the most typical items used with flow racks. They should be sturdy and have a flat bottom to facilitate easy sliding.
2. **Totes and Bins**: Plastic or metal totes and bins are ideal for flow racks, especially when they are used for storing smaller items that need to be grouped together.
3. **Trays**: Trays with flat bottoms can be used to transport items that might not be stable on their own, such as small parts or irregularly shaped products.
4. **Pallets**: In some heavy-duty flow rack systems, pallets can be used, provided the system is designed to handle the weight and size of pallets.
5. **Cases**: Pre-packaged cases of products, such as beverages or canned goods, are suitable for flow racks, especially in retail and distribution settings.
6. **Tires**: Specialized flow racks can be used for storing and moving tires, particularly in automotive warehouses.
7. **Cylindrical Items**: Items like rolls of fabric or paper can be used with flow racks if they are placed in appropriate holders or trays to prevent rolling.
8. **Food Products**: Packaged food items, especially those in boxes or cartons, are commonly used in flow racks in grocery and food distribution centers.
9. **Pharmaceuticals**: In pharmaceutical settings, flow racks are used for storing and picking medications, typically in bins or cartons.
10. **Electronics**: Small electronic components can be stored in bins or trays on flow racks for easy access in manufacturing or assembly environments.
The key is that items should be stable, have a consistent shape, and be compatible with the flow rack's design to ensure efficient movement and storage.