Call +(254) 703 030 000 / 751 483 999 / 721 704 777
- Home
- Material Handling
- Lifting Pulling Positioning
- Hoists Trolleys
- Electric Hoists
.....Read More
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an electric hoist and how does it work?
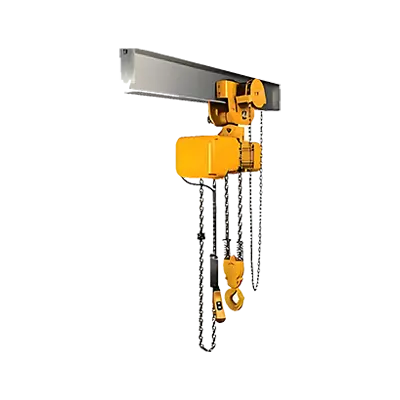
An electric hoist is a mechanical device used for lifting, lowering, and moving heavy loads with the aid of a motor. It is commonly used in industrial settings, construction sites, and warehouses to facilitate the handling of materials and equipment. The primary components of an electric hoist include an electric motor, a drum or lift-wheel, a wire rope or chain, a hook, and a control system.
The electric motor powers the hoist, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. This motor drives the drum or lift-wheel, which winds or unwinds the wire rope or chain. The wire rope or chain is attached to a hook that holds the load. The control system, often operated via a pendant control or remote control, allows the operator to manage the hoist's movements, including lifting, lowering, and stopping the load.
Electric hoists can be mounted in various configurations, such as fixed, trolley-mounted, or overhead, depending on the application and the required range of motion. They are available in different capacities, from small units for light loads to large models capable of lifting several tons.
The operation of an electric hoist involves engaging the motor to lift or lower the load. When the operator activates the control system, the motor turns the drum or lift-wheel, which either winds the rope or chain to lift the load or unwinds it to lower the load. Safety features, such as limit switches and overload protection, are often integrated to prevent accidents and ensure safe operation.
Overall, electric hoists provide an efficient, reliable, and safe method for handling heavy loads, reducing manual labor and increasing productivity in various industrial applications.
What are the advantages of using an electric hoist over a manual hoist?
Electric hoists offer several advantages over manual hoists, primarily in terms of efficiency, safety, and ease of use.
1. **Efficiency and Speed**: Electric hoists can lift loads much faster than manual hoists, significantly increasing productivity. They are capable of handling heavy loads with minimal effort, reducing the time required for lifting operations.
2. **Load Capacity**: Electric hoists generally have a higher load capacity compared to manual hoists. This makes them suitable for industrial applications where heavy lifting is required.
3. **Precision and Control**: Electric hoists provide precise control over lifting and lowering operations. They often come with variable speed controls, allowing for smooth and accurate positioning of loads.
4. **Reduced Physical Strain**: Operating an electric hoist requires minimal physical effort, reducing the risk of strain or injury to workers. This is particularly beneficial in environments where frequent lifting is necessary.
5. **Safety Features**: Electric hoists are equipped with advanced safety features such as overload protection, emergency stop functions, and limit switches, which enhance operational safety and prevent accidents.
6. **Consistency and Reliability**: Electric hoists offer consistent performance and are less prone to human error compared to manual hoists. They provide reliable operation, which is crucial in maintaining workflow efficiency.
7. **Versatility**: Electric hoists can be used in a variety of settings and are adaptable to different lifting requirements. They can be mounted in fixed positions or used with trolleys for horizontal movement.
8. **Remote Operation**: Many electric hoists can be operated remotely, allowing operators to control the hoist from a safe distance, further enhancing safety and convenience.
Overall, electric hoists are a superior choice for applications requiring frequent, heavy, or precise lifting, offering significant advantages in terms of speed, safety, and operational efficiency.
How do you choose the right electric hoist for your needs?
To choose the right electric hoist, consider the following factors:
1. **Load Capacity**: Determine the maximum weight the hoist needs to lift. Choose a hoist with a capacity slightly above your maximum requirement to ensure safety and efficiency.
2. **Lift Height**: Measure the vertical distance the hoist needs to cover. Ensure the hoist's lift height exceeds this distance to accommodate any additional requirements.
3. **Power Source**: Decide between single-phase or three-phase power based on your facility's electrical setup. Ensure compatibility to avoid additional installation costs.
4. **Speed**: Consider the lifting speed required for your operations. Faster speeds increase productivity but may require more power and control precision.
5. **Duty Cycle**: Evaluate the frequency and duration of use. Choose a hoist with a duty cycle that matches your operational demands to prevent overheating and wear.
6. **Control System**: Decide between pendant controls, wireless remote controls, or integrated systems based on convenience and safety needs.
7. **Environment**: Consider environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances. Select a hoist with appropriate protection ratings and materials.
8. **Mounting Options**: Choose between hook-mounted, trolley-mounted, or stationary hoists based on your workspace layout and mobility needs.
9. **Safety Features**: Look for features like overload protection, emergency stop functions, and limit switches to enhance safety.
10. **Brand and Warranty**: Opt for reputable brands known for reliability and support. Check warranty terms for coverage and service options.
11. **Budget**: Balance cost with features and quality. Consider long-term maintenance and operational costs in addition to the initial purchase price.
By evaluating these factors, you can select an electric hoist that meets your specific operational requirements and ensures safety and efficiency.
What maintenance is required for electric hoists?
Electric hoists require regular maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operation. Key maintenance tasks include:
1. **Inspection**: Regularly inspect the hoist for any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Check the load chain or wire rope for kinks, twists, or broken strands. Inspect the hooks for deformation or cracks.
2. **Lubrication**: Proper lubrication of the load chain or wire rope is essential to reduce friction and wear. Use the manufacturer-recommended lubricant and apply it at regular intervals.
3. **Electrical Components**: Check the electrical connections, wiring, and control systems for any signs of damage or wear. Ensure that the control pendant and emergency stop functions are working correctly.
4. **Brakes**: Test the hoist's braking system to ensure it engages and releases properly. Adjust or replace brake components as needed to maintain optimal performance.
5. **Limit Switches**: Verify that the upper and lower limit switches are functioning correctly to prevent over-travel of the hoist.
6. **Load Testing**: Conduct periodic load tests to ensure the hoist can handle its rated capacity safely. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for load testing procedures.
7. **Cleaning**: Keep the hoist clean and free from dust, dirt, and debris. This helps prevent contamination of moving parts and electrical components.
8. **Documentation**: Maintain a detailed log of all inspections, maintenance activities, and repairs. This documentation helps track the hoist's condition and ensures compliance with safety regulations.
9. **Training**: Ensure that operators and maintenance personnel are properly trained in the use and maintenance of the hoist. Regular training updates can help prevent accidents and equipment damage.
10. **Manufacturer's Guidelines**: Always follow the manufacturer's maintenance schedule and guidelines for specific maintenance tasks and intervals.
Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the hoist but also ensures safety and reliability in lifting operations.
What are the safety precautions when using an electric hoist?
1. **Inspection**: Regularly inspect the hoist for any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Check the hooks, chains, and cables for integrity.
2. **Load Limits**: Never exceed the hoist's rated load capacity. Always know the weight of the load being lifted.
3. **Training**: Ensure operators are properly trained and familiar with the hoist's operation and safety features.
4. **Environment**: Use the hoist in a safe environment, free from obstructions and hazards. Ensure the area is well-lit and clear of unnecessary personnel.
5. **Load Attachment**: Securely attach the load to the hoist using appropriate slings or attachments. Ensure the load is balanced and stable before lifting.
6. **Operation**: Operate the hoist smoothly, avoiding sudden starts, stops, or jerks. Use the controls as intended and avoid using the hoist for side pulling.
7. **Emergency Procedures**: Be familiar with emergency stop procedures and ensure the hoist has accessible emergency stop controls.
8. **Maintenance**: Follow the manufacturer's maintenance schedule and guidelines. Keep records of all maintenance activities.
9. **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves, hard hats, and safety shoes, to protect against potential hazards.
10. **Communication**: Maintain clear communication with all personnel involved in the lifting operation. Use hand signals or radios if necessary.
11. **Power Supply**: Ensure the hoist is connected to the correct power supply and that all electrical components are in good condition.
12. **Lockout/Tagout**: Implement lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance or when the hoist is not in use to prevent accidental operation.
13. **Weather Conditions**: Avoid using the hoist in adverse weather conditions that could affect safety, such as high winds or lightning.
14. **Documentation**: Keep all manuals, safety instructions, and inspection records readily available for reference.
How do you install an electric hoist?
1. **Select Location**: Choose a suitable location with adequate structural support to handle the hoist's load capacity.
2. **Gather Tools and Equipment**: Ensure you have the necessary tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, a drill, and safety gear.
3. **Install Mounting Bracket**: Securely attach the mounting bracket to the beam or ceiling using bolts. Ensure it is level and tightly fastened.
4. **Attach Hoist to Bracket**: Lift the hoist and attach it to the mounting bracket. Use the appropriate bolts and ensure they are tightened securely.
5. **Electrical Connection**: Connect the hoist to a power source. Ensure the power supply matches the hoist's voltage requirements. Use a qualified electrician if necessary.
6. **Install Control Pendant**: Attach the control pendant to the hoist. Ensure it is easily accessible and the cable is not tangled.
7. **Test Operation**: Power on the hoist and test its operation without a load. Check for smooth operation in both lifting and lowering.
8. **Load Test**: Gradually apply a load to test the hoist's lifting capacity. Ensure it operates smoothly and safely under load.
9. **Safety Checks**: Inspect all connections, bolts, and the hoist mechanism for any signs of wear or looseness. Ensure all safety features are functional.
10. **Regular Maintenance**: Establish a maintenance schedule to regularly inspect and service the hoist to ensure ongoing safety and functionality.
What are the common problems and troubleshooting tips for electric hoists?
Common problems with electric hoists include:
1. **Power Issues**:
- **Problem**: Hoist not starting or losing power.
- **Troubleshooting**: Check power supply, circuit breakers, and fuses. Ensure connections are secure.
2. **Overheating**:
- **Problem**: Motor overheating.
- **Troubleshooting**: Allow the motor to cool down. Check for overloading and ensure proper ventilation.
3. **Unusual Noises**:
- **Problem**: Grinding or squealing sounds.
- **Troubleshooting**: Inspect gears and bearings for wear. Lubricate moving parts as needed.
4. **Load Drifting**:
- **Problem**: Load not holding position.
- **Troubleshooting**: Check the brake system for wear or damage. Adjust or replace brake components.
5. **Slow Operation**:
- **Problem**: Hoist operating slower than normal.
- **Troubleshooting**: Inspect for mechanical obstructions. Check motor and gearbox for issues.
6. **Chain or Wire Rope Issues**:
- **Problem**: Chain or rope not feeding properly.
- **Troubleshooting**: Ensure proper alignment and tension. Inspect for kinks, twists, or damage.
7. **Control Problems**:
- **Problem**: Remote or pendant not functioning.
- **Troubleshooting**: Check for loose connections or damaged wires. Replace batteries or faulty components.
8. **Limit Switch Malfunction**:
- **Problem**: Hoist not stopping at limits.
- **Troubleshooting**: Adjust or replace limit switches. Ensure they are correctly positioned.
9. **Corrosion or Rust**:
- **Problem**: Corrosion affecting performance.
- **Troubleshooting**: Regularly clean and apply anti-corrosion treatments. Store in a dry environment.
10. **General Maintenance**:
- **Tip**: Regularly inspect and maintain all components. Follow manufacturer guidelines for servicing.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage and ensure safe operation.