Call +(254) 703 030 000 / 751 483 999 / 721 704 777
- Home
- Information Communication Network
.....Read More
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an information and communication network?
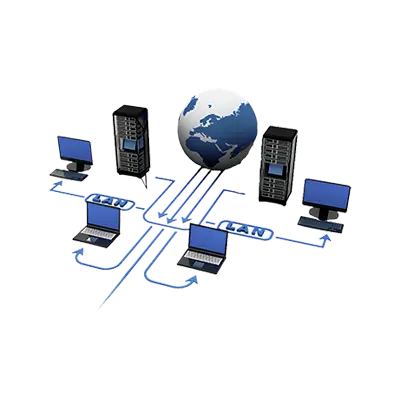
An information and communication network is a system that facilitates the exchange, processing, and storage of data and information among various entities. It comprises interconnected hardware, software, and communication protocols that enable the seamless transfer of data across different locations. These networks can be local, such as a Local Area Network (LAN) within a building, or global, like the Internet, which connects millions of devices worldwide.
The core components of an information and communication network include:
1. **Hardware**: This includes physical devices like computers, servers, routers, switches, and transmission media (cables, fiber optics, or wireless signals) that form the backbone of the network.
2. **Software**: Network operating systems, applications, and protocols (such as TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP) that manage data flow, ensure security, and provide user interfaces for interaction.
3. **Data**: The raw information that is processed and transmitted across the network, which can be in the form of text, audio, video, or other digital formats.
4. **Users**: Individuals or systems that interact with the network to send, receive, or manage information.
5. **Protocols**: Established rules and standards that govern data exchange, ensuring interoperability and communication efficiency between different network components.
Information and communication networks are essential for various applications, including business operations, education, healthcare, and entertainment. They enable real-time communication, resource sharing, and collaboration, significantly enhancing productivity and connectivity. Security measures, such as encryption and firewalls, are crucial to protect data integrity and privacy within these networks. As technology evolves, these networks continue to expand in capability and reach, driving innovation and transforming how information is accessed and utilized globally.
How does an information and communication network work?
An information and communication network functions by facilitating the exchange of data between devices, systems, or users through interconnected pathways. It comprises several key components: hardware, software, protocols, and transmission media.
1. **Hardware**: This includes devices like routers, switches, servers, and end-user devices (computers, smartphones). Routers direct data packets between networks, while switches connect devices within a network.
2. **Software**: Network operating systems and applications manage data flow and provide services like email, file sharing, and web browsing. Network management software monitors and optimizes performance.
3. **Protocols**: These are rules governing data exchange. Protocols like TCP/IP ensure reliable data transmission, while HTTP/HTTPS facilitate web communication. Protocols standardize communication, enabling interoperability between different devices and systems.
4. **Transmission Media**: Data travels through wired (Ethernet cables, fiber optics) or wireless (Wi-Fi, cellular) media. Wired connections offer high speed and reliability, while wireless provides mobility and convenience.
The network operates through a series of steps:
- **Data Generation**: Users create data using applications.
- **Data Packaging**: Data is divided into packets, each with a header containing destination and source addresses.
- **Data Transmission**: Packets are sent over the network via routers and switches, following the most efficient path.
- **Data Reception**: The receiving device reassembles packets into the original data.
- **Data Processing**: The data is processed by applications on the receiving device.
Security measures like firewalls, encryption, and authentication protect data integrity and privacy. Networks can be local (LAN), wide-area (WAN), or global (Internet), each varying in scale and complexity. The seamless integration of these components ensures efficient and reliable communication across diverse platforms and locations.
What are the components of an information and communication network?
An information and communication network comprises several key components that work together to facilitate the exchange of data and information. These components include:
1. **Hardware**: This includes physical devices such as computers, servers, routers, switches, modems, and other networking equipment that form the backbone of the network infrastructure.
2. **Software**: Network management software, operating systems, and applications that enable communication and data processing. This includes protocols and services that manage data flow and ensure secure and efficient communication.
3. **Transmission Media**: The physical pathways through which data is transmitted. This can be wired (e.g., Ethernet cables, fiber optics) or wireless (e.g., Wi-Fi, cellular networks).
4. **Network Protocols**: Rules and conventions for communication between network devices. Protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP, and SMTP ensure data is transmitted accurately and efficiently.
5. **Data**: The actual information being communicated, which can include text, audio, video, and other digital formats.
6. **Network Services**: Services that support network operations, such as DNS (Domain Name System), DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), and email services.
7. **Security Measures**: Tools and protocols to protect data integrity and privacy, including firewalls, encryption, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems.
8. **Users and End Devices**: The individuals and devices (e.g., computers, smartphones, tablets) that access and utilize the network for communication and information exchange.
9. **Network Architecture**: The design and structure of the network, including topology (e.g., star, mesh, bus) and the arrangement of devices and connections.
10. **Cloud Services**: Increasingly, networks incorporate cloud-based resources and services, providing scalable and flexible access to data and applications.
These components collectively enable the seamless transmission and reception of information across various platforms and locations.
What are the layers of an information and communication network?
1. **Physical Layer**: This is the foundational layer that includes the hardware components such as cables, switches, routers, and other physical devices that facilitate data transmission. It deals with the physical connection between devices and the transmission of raw binary data over a medium.
2. **Data Link Layer**: This layer is responsible for node-to-node data transfer and error detection and correction. It ensures that data is transferred reliably over the physical layer by managing protocols like Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
3. **Network Layer**: This layer manages the routing of data packets between devices across different networks. It determines the best path for data transfer and handles logical addressing through IP addresses.
4. **Transport Layer**: This layer ensures complete data transfer and error recovery. It provides end-to-end communication services for applications and manages data flow control, segmentation, and reassembly. Protocols like TCP and UDP operate at this layer.
5. **Session Layer**: This layer manages sessions or connections between applications. It establishes, maintains, and terminates connections, ensuring that data exchange is properly synchronized.
6. **Presentation Layer**: This layer translates data between the application layer and the network. It handles data encryption, compression, and translation, ensuring that data is in a readable format for the application layer.
7. **Application Layer**: This is the topmost layer that interacts directly with end-users. It provides network services to applications, such as email, file transfer, and web browsing, through protocols like HTTP, FTP, and SMTP.
How do information and communication networks support cloud computing?
Information and communication networks are fundamental to cloud computing, providing the infrastructure necessary for data transmission, storage, and processing. These networks enable seamless connectivity between cloud service providers and users, ensuring efficient access to cloud resources.
Firstly, high-speed internet and broadband networks facilitate rapid data transfer between users and cloud servers. This is crucial for real-time applications and services, allowing users to access and manipulate data stored in the cloud with minimal latency.
Secondly, data centers, which are the backbone of cloud computing, rely on robust communication networks to interconnect multiple servers and storage systems. These networks ensure that data is efficiently distributed and replicated across different locations, enhancing reliability and availability.
Thirdly, advanced networking technologies like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) optimize network resources and improve scalability. SDN allows for dynamic network management, enabling cloud providers to adjust network configurations in real-time to meet changing demands. NFV, on the other hand, virtualizes network services, reducing the need for physical hardware and allowing for more flexible and cost-effective network management.
Moreover, communication protocols such as HTTP/HTTPS, TCP/IP, and APIs facilitate interaction between cloud services and users. These protocols ensure secure and reliable data exchange, which is essential for maintaining data integrity and privacy.
Lastly, edge computing, an extension of cloud computing, leverages local networks to process data closer to the source. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, enhancing the performance of cloud services, especially for IoT applications.
In summary, information and communication networks provide the essential infrastructure and technologies that enable cloud computing to function efficiently, securely, and at scale, supporting a wide range of applications and services.
What security measures are used in information and communication networks?
Information and communication networks employ a variety of security measures to protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. These measures include:
1. **Encryption**: Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest using protocols like SSL/TLS for secure communication and AES for data storage, ensuring that unauthorized parties cannot access sensitive information.
2. **Firewalls**: Firewalls act as barriers between trusted and untrusted networks, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules to prevent unauthorized access.
3. **Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)**: These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and can take action to block or alert administrators about potential threats.
4. **Access Control**: Implementing strong authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized users can access specific network resources.
5. **Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)**: VPNs create secure, encrypted connections over the internet, allowing remote users to access the network safely.
6. **Antivirus and Anti-malware Software**: These programs detect, prevent, and remove malicious software from devices and networks, protecting against viruses, worms, and other malware.
7. **Patch Management**: Regularly updating software and systems to fix vulnerabilities helps protect against exploits and attacks.
8. **Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)**: SIEM systems collect and analyze security data from across the network, providing real-time insights and alerts for potential security incidents.
9. **Data Loss Prevention (DLP)**: DLP technologies monitor and control data transfer to prevent unauthorized data exfiltration.
10. **Network Segmentation**: Dividing the network into segments limits the spread of attacks and restricts access to sensitive areas.
11. **User Education and Training**: Regular training programs for employees on security best practices and awareness help mitigate risks from human error and social engineering attacks.
These measures, when combined, create a robust security posture that helps protect information and communication networks from a wide range of threats.
How do information and communication networks impact daily life?
Information and communication networks profoundly impact daily life by enhancing connectivity, accessibility, and efficiency. They enable instant communication through emails, messaging apps, and social media, allowing people to connect globally in real-time. This connectivity fosters personal relationships and facilitates professional collaborations, breaking geographical barriers.
In education, these networks provide access to vast resources and online learning platforms, enabling lifelong learning and skill development. Students and educators can access information, participate in virtual classrooms, and collaborate on projects, enhancing the educational experience.
In the workplace, communication networks streamline operations through tools like video conferencing, cloud computing, and project management software. This leads to increased productivity, remote work opportunities, and flexible work environments, contributing to a better work-life balance.
E-commerce and online banking, powered by these networks, offer convenience and efficiency in shopping and financial transactions. Consumers can compare products, read reviews, and make purchases from anywhere, while businesses can reach a broader audience.
Healthcare benefits from telemedicine and electronic health records, improving patient care and access to medical services. Patients can consult with healthcare providers remotely, reducing the need for physical visits and enhancing healthcare delivery.
Socially, these networks influence culture and society by shaping public opinion and enabling social movements. They provide platforms for sharing ideas, raising awareness, and mobilizing support for various causes.
However, the pervasive nature of these networks also raises concerns about privacy, security, and digital divide. Ensuring equitable access and safeguarding personal information are critical challenges that need addressing.
Overall, information and communication networks are integral to modern life, driving innovation and transforming how individuals interact, work, learn, and access services.
What are the challenges faced by information and communication networks?
Information and communication networks face several challenges:
1. **Security Threats**: Networks are vulnerable to cyberattacks such as hacking, phishing, and malware, which can lead to data breaches and loss of sensitive information.
2. **Scalability**: As the number of connected devices increases, networks must scale efficiently to handle more traffic without compromising performance.
3. **Bandwidth Limitations**: High demand for data-intensive applications can strain network bandwidth, leading to congestion and slower speeds.
4. **Interoperability**: Diverse technologies and standards can create compatibility issues, making it difficult for different systems to communicate effectively.
5. **Latency**: Delays in data transmission can affect real-time applications like video conferencing and online gaming, requiring networks to minimize latency.
6. **Reliability and Downtime**: Networks must ensure high availability and minimize downtime to maintain user trust and business continuity.
7. **Cost Management**: Upgrading infrastructure and maintaining networks can be expensive, requiring efficient cost management strategies.
8. **Regulatory Compliance**: Networks must adhere to various legal and regulatory requirements, which can vary by region and industry.
9. **Energy Consumption**: As networks grow, so does their energy consumption, raising concerns about sustainability and environmental impact.
10. **Quality of Service (QoS)**: Ensuring consistent and high-quality service for all users, especially during peak times, is a significant challenge.
11. **Data Privacy**: Protecting user data and ensuring privacy in communication networks is critical, especially with increasing data collection and surveillance concerns.
12. **Technological Advancements**: Keeping up with rapid technological changes and integrating new technologies can be challenging for network providers.
13. **Infrastructure Limitations**: In some regions, inadequate infrastructure can hinder network performance and accessibility.
Addressing these challenges requires continuous innovation, investment, and strategic planning to ensure robust, secure, and efficient network operations.
How do information and communication networks ensure data privacy?
Information and communication networks ensure data privacy through a combination of technical, administrative, and legal measures.
1. **Encryption**: Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Protocols like TLS/SSL secure data during transmission, while encryption standards like AES protect stored data, ensuring only authorized parties can access it.
2. **Access Controls**: Networks implement strict access controls, using authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication to ensure only authorized users can access sensitive data.
3. **Data Minimization**: Networks limit data collection to only what is necessary for specific purposes, reducing the risk of exposure and misuse.
4. **Anonymization and Pseudonymization**: Techniques are used to remove or obscure personal identifiers from data sets, making it difficult to trace data back to individuals.
5. **Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)**: These tools monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking unauthorized access and detecting potential threats.
6. **Regular Audits and Monitoring**: Continuous monitoring and regular audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with privacy policies and regulations.
7. **Data Breach Response Plans**: Networks have protocols in place to quickly respond to data breaches, minimizing damage and notifying affected parties as required by law.
8. **Compliance with Regulations**: Adherence to data protection laws and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, ensures networks follow best practices for data privacy.
9. **User Education and Awareness**: Training programs for users and employees help them understand the importance of data privacy and how to protect sensitive information.
10. **Data Integrity and Backup**: Ensuring data integrity through checksums and regular backups prevents data loss and unauthorized alterations.
These measures collectively create a robust framework for protecting data privacy within information and communication networks.
What is the future of information and communication networks?
The future of information and communication networks is poised to be transformative, driven by advancements in technology and evolving user demands. Key trends include the expansion of 5G and the emergence of 6G, which promise ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity, enabling real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery. The Internet of Things (IoT) will proliferate, connecting billions of devices and generating vast amounts of data, necessitating robust network infrastructure and advanced data analytics.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning will play crucial roles in optimizing network performance, enhancing security, and personalizing user experiences. Edge computing will become more prevalent, processing data closer to the source to reduce latency and bandwidth usage, crucial for applications like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR).
Quantum computing, though in its nascent stages, holds potential to revolutionize network security and data processing capabilities. Blockchain technology may offer decentralized solutions for secure data transactions and identity management.
Network architectures will evolve towards more software-defined and virtualized models, allowing for greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. This shift will support the growing demand for cloud services and facilitate seamless integration across diverse platforms.
Cybersecurity will remain a critical focus, with networks increasingly targeted by sophisticated cyber threats. Enhanced encryption, AI-driven threat detection, and zero-trust security models will be essential to protect sensitive information.
Sustainability will also be a priority, with efforts to reduce the carbon footprint of network operations through energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources.
Overall, the future of information and communication networks will be characterized by increased connectivity, intelligence, and adaptability, driving innovation across industries and enhancing global communication.