- Home
- Electrical
- Cables Conductors
- Instrumentation And Control Cables
.....Read More
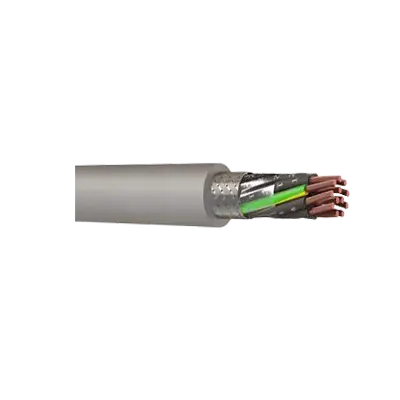

CY Multicore Screened Control Cable
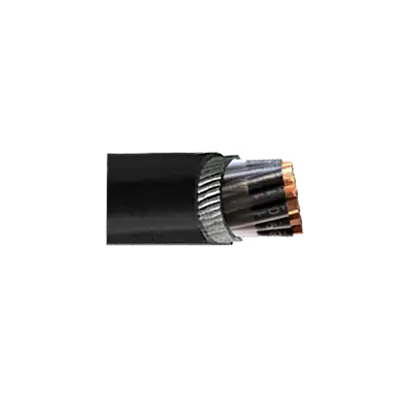

Multicore Control Cable - Armoured
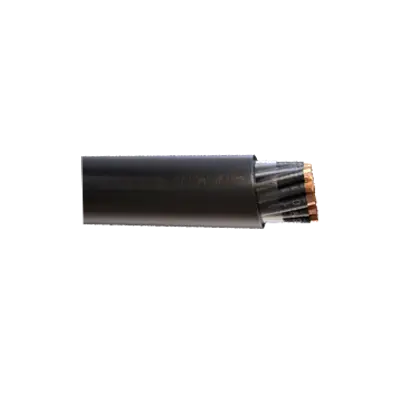

Multicore Control Cable - Unarmoured
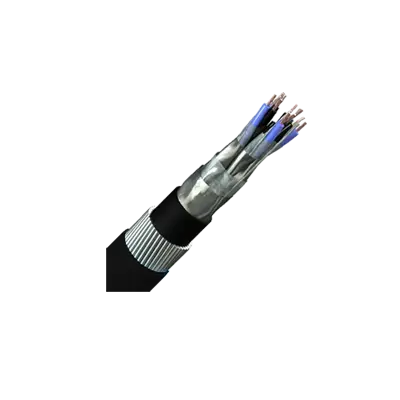
Overall & Individually Screened Armoured Instrumentation Cables
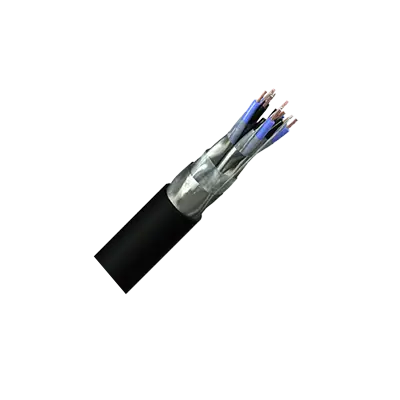
Overall & Individually Screened Unarmoured Instrumentation Cables
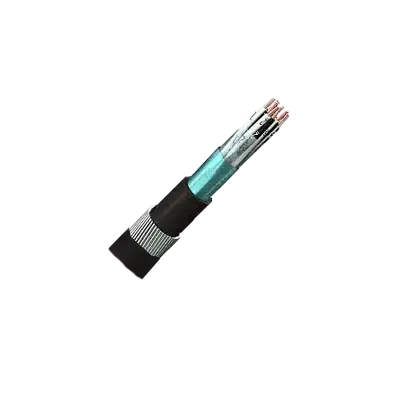

Overall Screened Armoured Instrumentation Cables
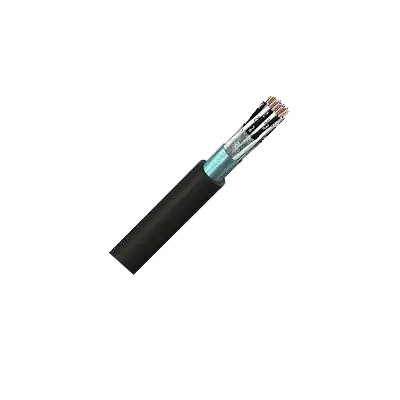

Overall Screened Unarmoured Instrumentation Cables
Frequently Asked Questions
What are instrumentation and control cables used for?
What are the key differences between instrumentation cables and control cables?
How do you select the right instrumentation and control cable for a specific application?
What are the common materials used in the construction of instrumentation and control cables?
How do shielding and insulation affect the performance of instrumentation and control cables?
What are the standards and certifications for instrumentation and control cables?
How do you install and maintain instrumentation and control cables to ensure optimal performance?