- Home
- Electrical
- Cables Conductors
- Aluminium Cables
.....Read More
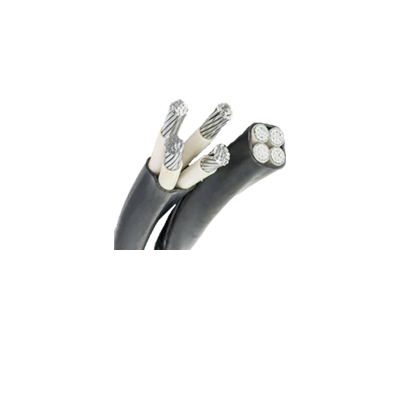

Aerial Bundled Cable - Low Voltage
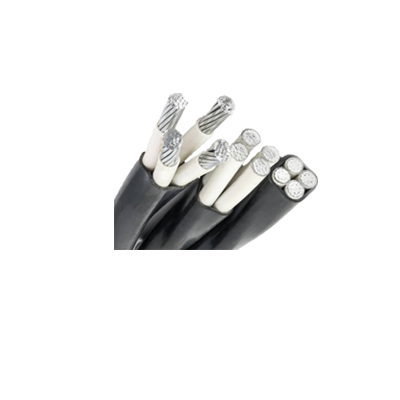

Aerial Bundled Cable - Medium Voltage

High Voltage Power Cable (>= 66kV) - Armoured
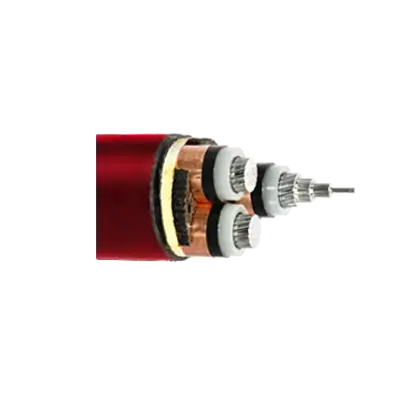
High Voltage Power Cable ( >=66kV) - Unarmoured

Low Voltage Power Cable (<= 3.3kV) - Armoured
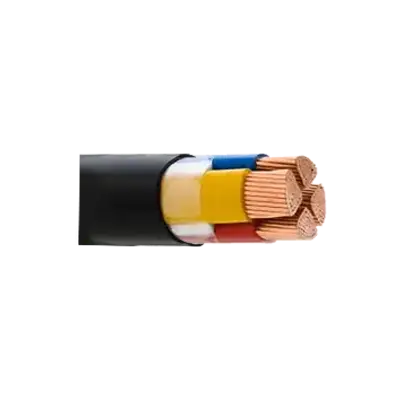
Low Voltage Power Cable (<= 3.3kV) - Unarmoured
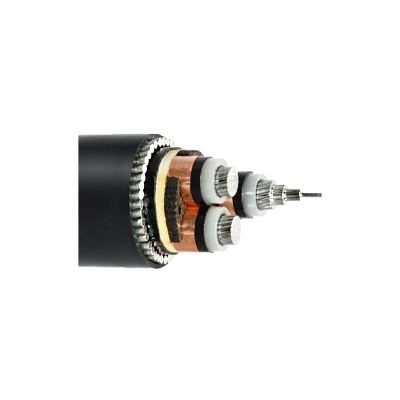
Medium Voltage Power Cable (>6kV - 33kV) - Armoured

Medium Voltage Power Cable ( >6kV - 33kV)- Unarmoured
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the advantages of using aluminium cables over copper cables?
2. How do you prevent galvanic corrosion in aluminium cable connections?
3. What are the common applications of aluminium cables in electrical systems?
4. How does the conductivity of aluminium compare to copper in electrical cables?
5. What are the safety considerations when installing aluminium cables?
6. How do you properly terminate aluminium cables to prevent issues?
7. What maintenance is required for systems using aluminium cables?