- Home
- Tools
- Power Tools
- Power Saws Blades
- Power Saw Blades
.....Read More

Air-Powered Reciprocating Saw Blades

Band Saw Blade Coil Stock

Band Saw Blade Welders

Blades for Portable Band Saws

Ceramic, Composites & Cast Iron Cutting Welded Band Saw Blades

Circular Saw Blades

Cold Saw Blades

Concrete Chain Saw Chains & Bars

Corded & Cordless Reciprocating Saw Blades

Dado Sets

Diamond Saw Blades

Drywall-Cutting Hole Saws
Food-Cutting Skinner Blades

Food-Cutting Welded Band Saw Blades

Hole Saw Arbors & Pilot Drill Bits

Hole Saw & Hole Cutter Cases & Chip Collectors

Jigsaw Blades
Jigsaw Blade Sets
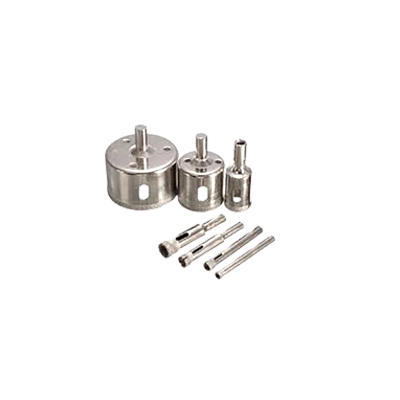

Masonry & Tile-Cutting Hole Saw Kits
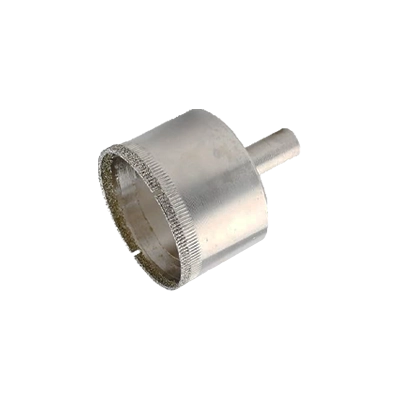

Masonry & Tile-Cutting Hole Saws
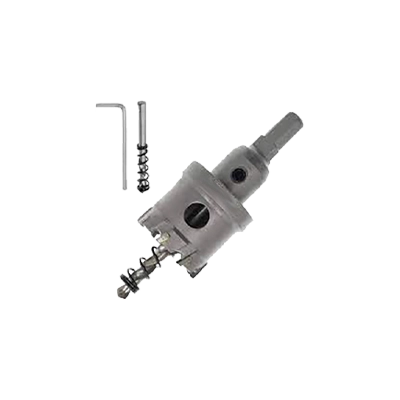

Metal-Cutting Hole Cutter Kits
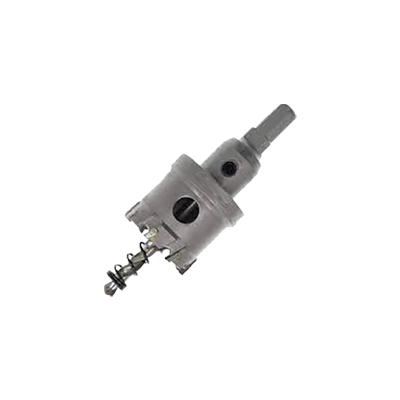

Metal-Cutting Hole Cutters
Metal-Cutting Welded Band Saw Blades
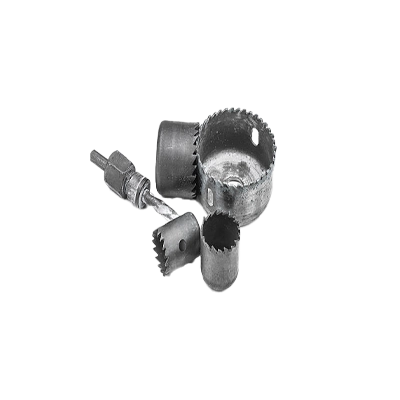

Multi-Material-Cutting Hole Saw Kits

Multi-Material-Cutting Hole Saws

Power Hacksaw Blades
Reciprocating Saw Blade Sets
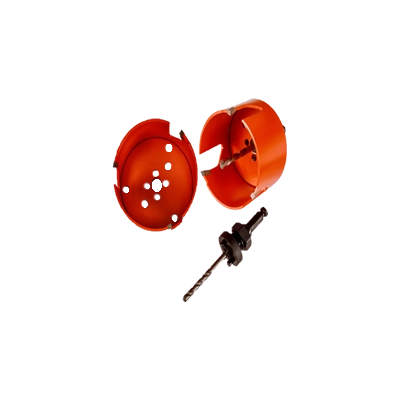

Rough-In Hole Saw Kits for Wood
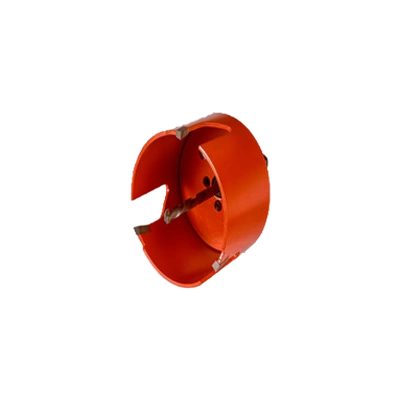

Rough-In Hole Saws for Wood

Scroll Saw Blades
Wood-Cutting Welded Band Saw Blades
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of power saw blades and their uses?
How do I choose the right saw blade for my project?
What is the difference between a circular saw blade and a reciprocating saw blade?
How often should I replace my power saw blade?
What materials can diamond blades cut?
How do I maintain and clean my saw blades?
What are the safety precautions when using power saw blades?