- Home
- Tools
- Power Tools
- Power Saws Blades
- Masonry Saws Tile Saws Concrete Saws
.....Read More

Corded Handheld Concrete Saws

Corded Tile Saws
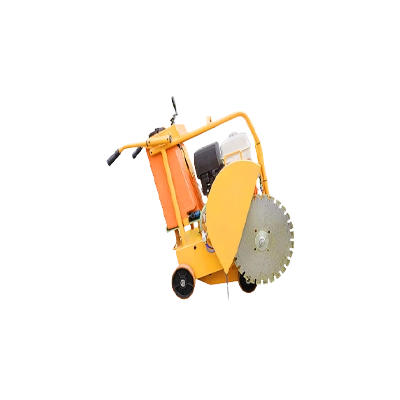
Corded Walk-Behind Concrete Saws

Cordless Handheld Concrete Saws

Cordless Walk-Behind Concrete Saws

Flooring Saws

Gas-Powered Concrete Chain Saws

Gas-Powered Handheld Concrete Saws

Gas-Powered Walk-Behind Concrete Saws

Handheld Concrete Saw Accessories

Masonry Saws

Replacement Parts for Masonry, Tile & Concrete Saws
Tile Saw Accessories
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a masonry saw and a tile saw?
How do I choose the right diamond blade for cutting concrete?
What safety precautions should be taken when using a concrete saw?
How do I maintain and clean a masonry saw?
Can a tile saw be used to cut other materials like stone or brick?
What is the best way to cut reinforced concrete?
How do I troubleshoot common issues with a walk-behind concrete saw?