.....Read More

Analog Panel Meters
Counter & Hour Meter Accessories

Counters, Hour Meters & Totalizers

Current Transducers

Digital Panel Meters

Energy Meters

Mechanical & Electronic Position Indicators
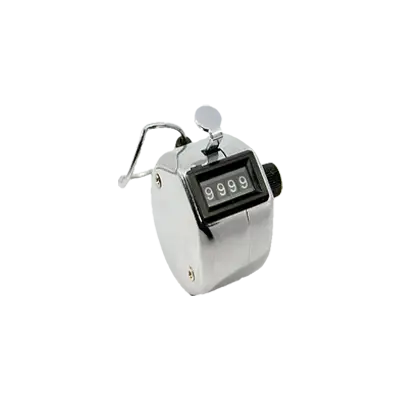

Mechanical & Hand Tally Counters

Mechanical Solenoids
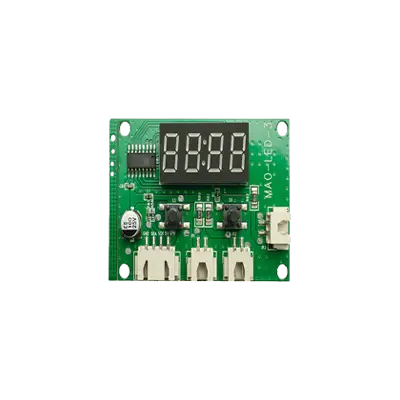

Panel Meter Accessories
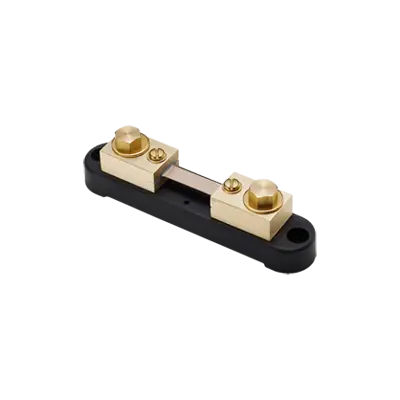

Panel Meter Shunts

PC and Work Station Enclosures
Pendant Arm System Components
Powder & Bulk Level Control Accessories

Powder & Bulk Level Controls
Pulse Generators

Rotary Encoder Accessories

Rotary Encoders

Signal Conditioners
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of using meters and counters in manufacturing?
How do counters help in tracking production output?
What are the benefits of using hour meters for heavy-duty equipment?
How can meters and counters improve facility efficiency?
What types of counters are commonly used in manufacturing?
How do hour meters estimate service times for equipment?
What factors should be considered when selecting meters and counters for a facility?